Installation: Difference between revisions
m (→Data Disk Mode) |
Prabuanand (talk | contribs) m (fixed broken link) |
||
| (394 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:hdd_mount.png|left|link=]] | [[Image:hdd_mount.png|left|link=]] | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
This page exists to provide a basic overview to get started. Before actually installing, it can help to skim through the [[Alpine_Linux:FAQ| Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)]], as well as to refer to the official installation guide at [https://docs.alpinelinux.org/ docs.alpinelinux.org]. | |||
{{Tip|This is a wiki! | |||
If something isn't correct, or is incomplete, you will have to figure it out, or ask for the correct solution in the [https://alpinelinux.org/community/ community]. | |||
And then carefully edit the wiki page. | |||
Just as those before who did it for you.}} | |||
== Minimal Hardware Requirements == | == Minimal Hardware Requirements == | ||
{{Main|Requirements}} | |||
* At least 128 MB of RAM. [A graphical desktop system may require up to 512 minimum.]. Note that an installation itself (from ISO) generally requires at least 320 MB during installation. | |||
* At least 0-700 MB space on a writable storage device. [Only required in [[#System Disk Mode|"sys"]] or [[#Data Disk Mode|"data"]] mode installations. It is optional in [[#Diskless Mode|"diskless"]] mode, where it may be used to save newer data and configurations states of a running system.] | |||
* A working internet connection is required to complete [[#System Disk Mode|"sys"]] mode installation. | |||
{{Note| Most of the steps outlined on this page applies to all [[:Category:Architectures|Architectures]] supported by Alpine Linux. For more specific installation instructions, refer to their respective pages. Refer [[#Custom Installation Instructions|custom installation instructions]] for headless system, virtualization etc.}} | |||
== Installation Overview == | == Installation Overview == | ||
Alpine Linux can be installed and run in [[Setting_up_disks_manually#Alpine_Linux_modes|three modes]] i.e [[#Diskless_Mode|Diskless Mode]], [[#Data_Disk_Mode|Data Disk Mode]] and [[#System_Disk_Mode|System Disk Mode]]. The installation procedure for Alpine Linux '''requires basic understanding of the three modes''' explained in brief below: | |||
[ | |||
==== Diskless Mode ==== | |||
{{Main|Diskless Mode}} | |||
In Diskless mode the entire operating system with all applications are first loaded into RAM and then only run from there. This mode is extremely fast and can save on unnecessary disk spin-ups, power, and wear. Alpine Linux uses this method to boot the .iso installation images. The [[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|<code>setup-alpine</code>]] script configures the installed system to continue to boot like this if "disk=none" is specified. | |||
==== Data Disk Mode ==== | |||
{{Main|Data Disk Mode}} | |||
In Data Disk mode also the operating system runs from system RAM, thus it enjoys the same accelerated operation speed as "diskless" mode. However, swap storage and the entire {{Path|/var}} directory tree get mounted from a persistent storage device. This mode is useful for having RAM accelerated servers with variable amounts of user-data that exceed the available RAM size. | |||
==== System Disk Mode ==== | |||
''' | System or '''sys''' Disk Mode is the traditional hard-disk install. Alpine Linux can be installed to an entire [[#setup-alpine based System Disk Install|'''hard disk''']] using <code>setup-alpine</code> script or to custom partitions using [[Setting_up_disks_manually|<code>setup-disk</code>]]. For further info, refer [[Setting_up_disks_manually|System Disk Mode]]. | ||
=== General course of action === | |||
It is really helpful for many use cases to [[#Preparing_for_the_installation|prepare]] and complete the [[#Installation_Step_Details|Installation]] until the [[#Base_configuration|base configuration]] step, then proceed with installation of the target system with any one of the various [[#Alternate courses of action|alternate]] courses of action. | |||
=== Alternate courses of action === | |||
Examples of preparation options: | |||
* Download some specific driver to configure the hardware, and/or install some software tool that may be missing in the live system by using the alpine package manager <code>[[Alpine_Package_Keeper|apk]]</code>. | |||
* Do a [[Setting_up_disks_manually#Manual_partitioning|Manual partitioning]] of the harddisk that avoids overwrite of an entire disk. | |||
Examples of proceeding options: | |||
* To install Alpine Linux on an '''entire hard disk''' with optional [[Alpine_setup_scripts#Environment_Variables|environment variables]], proceed to [[#setup-alpine_based_System_Disk_Install|setup-alpine based System Disk Install]]. | |||
* Use <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-lbu|setup-lbu]]</code> to configure a "local backup" location and <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-apkcache|setup-apkcache]]</code> to configure a local package cache storage location for the [[#Diskless Mode|diskless]] system and finally use <code>[[Alpine_local_backup|lbu commit]]</code> to then save the local configuration state. | |||
* Use <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-bootable|setup-bootable]]</code> to create a [[Create_a_Bootable_Device#Using_setup-bootable|customizable boot media]] for '''[[Installation#Diskless_Mode|diskless]]''' or '''[[Installation#Data_Disk_Mode|data]]''' disk-mode i.e a boot device with a writable filesystem. | |||
* Use <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-disk|setup-disk]]</code> to complete a [[Setting_up_disks_manually|traditional hard-disk installation]] on a partition or to [[Dualbooting|Dualboot]] or to configure [[Setting_up_disks_manually#RAID|RAID]], [[Setting_up_disks_manually#Encryption|encryption]] or [[Setting_up_disks_manually#LVM|LVM]] for both [[#Data Disk Mode|"data"]] disk and [[#System_Disk_Mode|"system"]] disk mode or to add a [[#Data Disk Mode|"data"]] mode partition. | |||
There are many more [[Alpine_setup_scripts|setup-scripts]] available. All these tools may also be run later to adjust specific configurations. For example, to set up a graphical environment as covered under [[Installation#Post-Installation|Post-Installation]] below. | |||
=== | == Preparing for the installation == | ||
=== Downloading installation image === | |||
Download the [https://alpinelinux.org/downloads/ stable-release installation image-file] for the target computer's architecture with their corresponding <code>sha256</code> (checksum) and <code>GPG</code> (signature) files. | |||
{{Note|Download <code>sha256</code> (checksum) and <code>GPG</code> (signature) files only from [https://alpinelinux.org/downloads/ official] site and not from mirrors.}} | |||
Now you have three files of the following format.. | |||
<pre> | |||
alpine-standard-*.iso | |||
alpine-standard-*.iso.sha256 | |||
alpine-standard-*.iso.asc | |||
</pre> | |||
''alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso'' is the '''3.20.3''' version '''Standard''' image file in '''iso''' format for '''x86_64''' architecture. Image file can also be '''gz''' for certain cases. | |||
=== Verifying downloaded image === | |||
From Security point of view, verify the downloaded image file for both checksum and GPG signature before proceeding further. The three required utilities i.e <code>sha256</code>, <code>curl</code> and <code>gpg</code> or their equivalents are available in every operating system including Linux, windows, Mac and BSD derivaties. | |||
{{Tip|Ensure that all the three downloaded files remain in the same folder. If not, adjust the commands accordingly.}} | |||
The <code>sha256</code> checksum verifies the integrity of the downloaded image i.e no modifications occurred during download. | |||
{{Cmd|sha256sum -c alpine-*.iso.'''sha256'''}} | |||
The <code>GPG</code> signature verifies the link between the downloaded image to the individual who signed it. Signature verification involves two steps: | |||
Step 1. Download and import the gpg signature from official website | |||
{{Cmd|curl https://alpinelinux.org/keys/ncopa.asc | gpg --import ;}} | |||
Step 2. Verify that the image signature matches with the one downloded in Step 1. | |||
{{Cmd|gpg --verify alpine-*.iso.'''asc''' alpine-*.'''iso'''}} | |||
=== | === Preparing installation media === | ||
{{Seealso|Burning ISOs}} | |||
{| | {{Note|These instructions are exclusively for x86_64 and x86. For ARM boards, see [[Alpine on ARM#Preparing installation media|Alpine on ARM]].}} | ||
| | |||
All data currently on the installation media will be '''lost''', when Alpine Linux installation image is written on it. Be extremely careful to correctly identify the device name for the installation media using the commands <code>lsblk</code> and <code>blkid</code>. | |||
In Linux, <code>dd</code> command can write the downloaded image file to the installation media i.e target device. | |||
{{Note|Modify the input file('''if''') and output file('''of''') according to the name and path to your image file and target device. Do not use partition numbers for the target device i.e use '''/dev/sdX''' instead of '''/dev/sdbXY.}} | |||
{{Cmd|# dd if{{=}}alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso of{{=}}/dev/sdX bs{{=}}4M status{{=}}progress; eject /dev/sdX}} | |||
If your version of <code>dd</code> does not support the option "status=progress", remove it. The <code>eject</code> command removes the target device from the system and ensures the write cache is completely flushed. | |||
In Windows, [https://rufus.ie/ Rufus] has been tested to create bootable USB flash drives and worked for Alpine Linux 3.12.x with the following settings: | |||
* '''Partition scheme''': <code>MBR</code> '''Target system''': <code>BIOS or UEFI</code> | |||
* '''File system''': <code>FAT32</code> '''Cluster size''': <code>4096 bytes (default)</code> | |||
=== Verifying Installation media === | |||
After detaching and re-attaching the device, a bit-wise comparison can verify the data written to the device (instead of just data buffered in RAM). If the comparison terminates with an end-of-file error on the .iso file side, all the contents from the image have been written (and re-read) successfully: | |||
<pre> | |||
# cmp ~/Downloads/alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso /dev/sdX | |||
cmp: EOF on alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Booting Installation Media === | |||
Insert the [[#Preparing_installation_media|Installation media]] to a proper drive or port of the computer and turn the machine on, or restart it, if already running. | |||
{{Note| To successfully boot and install Alpine Linux, disable [[Alpine_and_UEFI#How_to_boot_unsigned_code?|secure boot]] in the BIOS. Once Alpine Linux is installed, this can be [[UEFI_Secure_Boot|enabled]].}} | |||
If the computer does not automatically boot from the desired device, one needs to bring up the boot menu and choose the media to boot from. Depending on the computer, the menu may be accessed by repeatedly pressing a key quickly when booting starts. Some computers require that you press the button ''before'' starting the computer and hold it down while the computer boots. Typical keys are: {{key|F9}}-{{key|F12}}, sometimes {{key|F7}} or {{key|F8}}. If these don't bring up the boot menu, it may be necessary to enter the BIOS configuration and adjust the boot settings, for which typical keys are: {{key|Del}} {{key|F1}} {{key|F2}} {{key|F6}} or {{key|Esc}}. | |||
== Installation Step Details == | |||
=== Boot Process === | |||
The boot process of the alpine installation image first copies the entire operating system into the RAM memory, and then already starts a complete Alpine Linux system from there. It will initially only provide a basic command line environment that does not depend on reading from any (possibly slow) initial boot media, anymore. | |||
Local log-in is possible as the user <code>root</code>. Initially, the '''root''' user has no password. | |||
== | At the command prompt, an interactive script named [[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|<code>setup-alpine</code>]] is available to configure and install Alpine Linux. The script can be customized by the optional [[Alpine_setup_scripts#Environment_Variables|environment variables]], in case of [[Installation#Data_Disk_Mode|'''"data"''']] or [[Installation#System_Disk_Mode|'''"sys"''']] mode. For e.g {{Codeline|<code>USE_EFI{{=}}1 BOOTSIZE{{=}}512 setup-alpine</code>}}, sets the disklabel type to gpt, creates 512MB '''/boot''' partition with '''vfat''' filesystem and uses <code>grub</code> as bootloader. | ||
=== Base configuration === | |||
Launch the Alpine Linux Installation by running the [[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|<code>setup-alpine</code>]] script : | |||
{{Cmd|# setup-alpine}} | |||
The question-and-answer dialog of <code>setup-alpine</code> takes care of the base configuration. It sets up a network connection to access Internet to configure the system to boot into one of three different Alpine Linux "disk" modes: [[Installation#Diskless_Mode|'''"diskless"'''(none)]], [[Installation#Data_Disk_Mode|'''"data"''']] or [[Installation#System_Disk_Mode|'''"sys"''']]. If you choose to edit any option, the relevant file is opened in [[BusyBox#vi| '''vi''']] for editing. | |||
[[File:Installation-alpine-alpine-setup-3-setup-scripts.png|350px|thumb|right|Example <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|setup-alpine]]</code> session]] | |||
The <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|setup-alpine]]</code> script offers the following configuration options: | |||
# '''Keyboard Layout''' (Local keyboard language and usage mode, e.g. ''us'' and variant of ''us-nodeadkeys''.) | |||
# '''Hostname''' (The name for the computer.) | |||
# '''Network ''' (Setup network connection to access Internet.) | |||
#* Available interfaces are: '''eth0''' '''wlan0'''.(List depends on your hardware.) | |||
#* Which one do you want to initialize? (or '?' or 'done') [eth0] (Enter 'done' after configuring '''atleast''' one interface for Internet access.) | |||
#* Do you want to do any manual network configuration? (y/n) [n] (Default uses "DHCP".) | |||
# '''DNS Servers''' (If none of the interfaces configured in previous step uses dhcp, set DNS server. If unsure, leave DNS domain name blank and using <code>[https://quad9.net/ 9.9.9.9 2620:fe::fe]</code> for DNS is typically adequate.) | |||
# '''Root password''' (the password used to login to the root account) | |||
# '''Timezone''' (Optionally display times/dates in your local time zone) | |||
# '''HTTP/FTP Proxy''' (Proxy server to use for accessing the web/ftp. Use "none" for direct connections to websites and FTP servers.) | |||
# '''Mirror''' (From where to download packages. Choose the organization you trust giving your usage patterns to.) | |||
# '''Setup a user''' (Setting up a regular user account) | |||
# '''NTP''' (Network Time Protocol client used for keeping the system clock in sync with a time server. Package "chrony" is part of the default install image.) | |||
# '''SSH''' (Secure SHell remote access server. "OpenSSH" is part of the default install image. Use "none" to disable remote login, e.g. on laptops.) | |||
# In most cases, either one of following line(s) is displayed as follows: | |||
#: '''No disks found.''' or ''' Available disks are: sda (128.0 GB JMicron Tech )''' | |||
# '''Disk Mode''' ( A pre-setup of the "diskless" system or base configuration is completed by answering "none" when asked for the following questions.) | |||
#* Which disk(s) would you like to use? (or '?' for help or 'none') '''none''' | |||
#* Enter where to store configs (/media/ or 'none') '''none''' | |||
#* The location of the package cache '''none''' | |||
Base configuration is complete with the above step. Refer to the [[#Alternate courses of action|alternate courses of action]] to proceed further. | |||
=== setup-alpine based System Disk Install === | |||
<code>setup-alpine</code> script based installation, needs an ''' entire hard disk(s)''' for Alpine Linux and uses a partitioning layout with (/)root partition, /boot partition and a swap partition, where [[Alpine_setup_scripts#Environment_Variables|environment variables]] determine filesystem, size of the boot partition and the bootloader used. If your use case matches the above, at the final step of [[#Base configuration|base configuration]], type the appropriate hard disk '''device name''' instead of '''none'''. If multiple disks are chosen, [[Alpine_setup_scripts#RAID|RAID]] is used. | |||
* At the '''Disk Mode''' stage, '''sda''' or relevant disk(s) must be chosen in the below screen: | |||
** Which disk(s) would you like to use? (or '?' for help or 'none') '''sda''' | |||
** Confirmation for the chosen disk(s) appears. ''The following disk is selected:'' '''sda (128.0 GB JMicron Tech ).''' | |||
{{Warning|Pay close attention to the disk name and size. If you enter '''sys''' in the next step, no further questions will be asked and data on the chosen disk(s) will be overwritten!. Enter {{key|Ctrl}}+{{key|c}} to abort the installation process. Proceed only if you are 100% sure.}} | |||
* How would you like to use it? ('sys', 'data', 'lvm' or '?' for help) '''sys''' | |||
If '''sys''' is chosen, the <code>setup-alpine</code> script will complete the traditional hard-disk installation of Alpine Linux on the chosen disk(s) without further questions. Once the installation is complete, you can skip the next steps and proceed to [[#Reboot|reboot]] the system to boot into the newly installed Alpine Linux and [[Installation#Post-Installation|configure]] further. | |||
=== Custom partitioning === | |||
[[Setting_up_disks_manually#Manual_partitioning|Manual partitioning]] of the harddisk may be needed to prepare the harddisk for "sys" mode install using [[Setting_up_disks_manually|<code>setup-disk</code>]] and for storing the config file using [[Alpine_local_backup|<code>lbu commit</code>]] and package cache for [[Diskless Mode|Diskless]] and for /var mount for [[Data Disk Mode|Data disk]] mode installs. Refer [[Setting up disks manually|Setting up disks manually]] page for specific configurations related to [[Setting_up_disks_manually#RAID|RAID]], [[Setting_up_disks_manually#Encryption|encryption]], [[Setting_up_disks_manually#LVM|LVM]], etc... | |||
=== | === Preparing for the first boot === | ||
If [[#System_Disk_Mode|System Disk Mode]] of installation was performed, ignore this section and proceed to [[#Reboot|reboot]]. | |||
If the new local system was configured to run in "diskless" or "data" mode, and you do not want keep booting from the initial (and possibly read-only) [[Installation#Preparing_installation_media|installation media]], create a [[Create_a_Bootable_Device|customizable boot device]]. Once everything is in place, save your customized configuration with {{ic|lbu commit}} before rebooting. | |||
= | === Reboot === | ||
First, remove the initial installation media from the boot drive, or detach it from the port it's connected to. The system may now be power-cycled or rebooted to confirm everything is working correctly. The relevant commands for this are {{ic|poweroff}} or {{ic|reboot}}. Login into the new system with the root account. | |||
=== Completing the installation === | |||
The installation script installs only the base operating system. '''No''' applications e.g. web server, mail server, desktop environment, or web browsers are installed. | |||
Please look at [[Installation#Post-Installation|Post-Installation]], for some common things to do after installation. | |||
== Custom Installation Instructions == | |||
<!-- This has to be moved to headless installation page --> | |||
Custom-made headless apkovl can be done by first booting the install media on some computer with a display and keyboard attached, or in a virtual machine, and doing an intermediate "diskless" setup of just the boot media (more details below), i.e. using the offical <code>[[Alpine_setup_scripts#setup-alpine|setup-alpine]]</code> to configure the system's network, possibly for dhcp if needed, a ssh server, and a login user. Choosing "disks=none" for now, yet, configure to store configs on the boot media (if it is writable, otherwise on a separate storage media). And afterwards calling <code>[[Alpine_local_backup|lbu commit]]</code> to store the configs as local backup. Then your completed setup, including its securely created own private keys, will readily get (re)loaded on every subsequent (headless) boot from your custom-build <code><hostname>.apkovl.tar.gz</code> stored on the boot media (or on an auxilary media or server location, in case the boot media is read-only). | |||
* [[ | <!-- COMMENT FOR EDITORS | ||
Specific topics should be kept on separate pages and manageable category-pages only must get listed with direct reference on this general page. | |||
--> | |||
* [https://github.com/macmpi/alpine-linux-headless-bootstrap/ Bootstrap Alpine Linux on a headless system] using pre-built <code>apkovl</code> overlay file. | |||
* [[Kernels]] ''(kernel selection, e.g. for VMs or RPi)'' | |||
* [[How to make a custom ISO image with mkimage]] ''(installation media with its own configuration)'' | |||
* [[Directly booting an ISO file]] ''(without flashing it to a disk or device)'' | |||
* [[Netboot Alpine Linux using iPXE]] | |||
* [[:Category:Virtualization|Virtualization]] | |||
Also see other [[:Category:Installation|Installation Category]] pages. | |||
== Post-Installation == | |||
{{Tip|Alpine Linux packages stay close to the upstream design. Therefore, all upstream documentation about configuring a software package, as well as good configuration guides from other distributions that stay close to upstream, e.g. those in the [https://wiki.archlinux.org/ ArchWiki], or [https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/ Gentoo wiki] are to a large degree, also applicable to configuring the software on Alpine Linux, thus can be very useful.}} | |||
<!-- COMMENT FOR EDITORS | |||
If you edit Post-Install, | |||
* [[ | * Consider that there are already [[Tutorials_and_Howtos#Post-Install]], [[Developer_Documentation#Package_management]], {{:Daily driver guide}} and the Handbook, please work towards reducing duplication and providing an overview, and maintaining topic details of considerable size on their own pages. | ||
* Here, only the most relevant jumping off points are listed, not exact list duplicates!!! | |||
* Keep short-list of links here, as overview to more detailed topic specific pages. | |||
* Don't aggregate different topics at yet another place. | |||
--> | --> | ||
=== Daily driver guide === | |||
<!-- COMMENT FOR EDITORS | |||
Any topic related to configuring Alpine as Desktop workstation i.e as a daily driver must go to the [[Daily driver guide]] which is called below. Tutorial and How To should go to [[Tutorials_and_Howtos]]. | |||
--> | |||
{{:Daily driver guide}} | |||
=== Other topics === | |||
Topics not strictly related to using Alpine Linux as desktop are listed below: | |||
<!-- COMMENT FOR EDITORS | |||
* This section is meant to cover topics not related to Using Alpine as daily driver or as desktop workstation as there is already [[Daily driver guide]] and the Handbook. Please refer to the comment at the beginning of this wiki [[#Post-Installation]]. | |||
--> | |||
* [[Upgrading Alpine|Upgrade your OS]], when a new version is [https://www.alpinelinux.org/releases/ released]. | |||
* [[Tutorials_and_Howtos#Networking_2|Setting up Networking]] ''(including non-standard configurations)'' | |||
* [[OpenRC|Init System (OpenRC)]] ''(configure a service to automatically boot at next reboot)'' | |||
** [[Writing Init Scripts]] | |||
** [[Multiple Instances of Services]] | |||
* [[Hosting services on Alpine]] ''(links to several mail/web/ssh server setup pages)'' | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Tutorials and Howtos]] | |||
* [[Alpine_Linux:FAQ|FAQs]] | |||
= | * [[Comparison with other distros]] ''(how common things are done on Alpine)'' | ||
* [[Alpine_Linux:Wiki_etiquette|Wiki etiquette]] ''(to collaborate on this documentation)'' | |||
[[Category:Installation]] | [[Category:Installation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:06, 9 November 2024

This page exists to provide a basic overview to get started. Before actually installing, it can help to skim through the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), as well as to refer to the official installation guide at docs.alpinelinux.org.
If something isn't correct, or is incomplete, you will have to figure it out, or ask for the correct solution in the community.
And then carefully edit the wiki page.
Just as those before who did it for you.Minimal Hardware Requirements
- At least 128 MB of RAM. [A graphical desktop system may require up to 512 minimum.]. Note that an installation itself (from ISO) generally requires at least 320 MB during installation.
- At least 0-700 MB space on a writable storage device. [Only required in "sys" or "data" mode installations. It is optional in "diskless" mode, where it may be used to save newer data and configurations states of a running system.]
- A working internet connection is required to complete "sys" mode installation.
Installation Overview
Alpine Linux can be installed and run in three modes i.e Diskless Mode, Data Disk Mode and System Disk Mode. The installation procedure for Alpine Linux requires basic understanding of the three modes explained in brief below:
Diskless Mode
In Diskless mode the entire operating system with all applications are first loaded into RAM and then only run from there. This mode is extremely fast and can save on unnecessary disk spin-ups, power, and wear. Alpine Linux uses this method to boot the .iso installation images. The setup-alpine script configures the installed system to continue to boot like this if "disk=none" is specified.
Data Disk Mode
In Data Disk mode also the operating system runs from system RAM, thus it enjoys the same accelerated operation speed as "diskless" mode. However, swap storage and the entire /var directory tree get mounted from a persistent storage device. This mode is useful for having RAM accelerated servers with variable amounts of user-data that exceed the available RAM size.
System Disk Mode
System or sys Disk Mode is the traditional hard-disk install. Alpine Linux can be installed to an entire hard disk using setup-alpine script or to custom partitions using setup-disk. For further info, refer System Disk Mode.
General course of action
It is really helpful for many use cases to prepare and complete the Installation until the base configuration step, then proceed with installation of the target system with any one of the various alternate courses of action.
Alternate courses of action
Examples of preparation options:
- Download some specific driver to configure the hardware, and/or install some software tool that may be missing in the live system by using the alpine package manager
apk. - Do a Manual partitioning of the harddisk that avoids overwrite of an entire disk.
Examples of proceeding options:
- To install Alpine Linux on an entire hard disk with optional environment variables, proceed to setup-alpine based System Disk Install.
- Use
setup-lbuto configure a "local backup" location andsetup-apkcacheto configure a local package cache storage location for the diskless system and finally uselbu committo then save the local configuration state. - Use
setup-bootableto create a customizable boot media for diskless or data disk-mode i.e a boot device with a writable filesystem. - Use
setup-diskto complete a traditional hard-disk installation on a partition or to Dualboot or to configure RAID, encryption or LVM for both "data" disk and "system" disk mode or to add a "data" mode partition.
There are many more setup-scripts available. All these tools may also be run later to adjust specific configurations. For example, to set up a graphical environment as covered under Post-Installation below.
Preparing for the installation
Downloading installation image
Download the stable-release installation image-file for the target computer's architecture with their corresponding sha256 (checksum) and GPG (signature) files.
sha256 (checksum) and GPG (signature) files only from official site and not from mirrors.Now you have three files of the following format..
alpine-standard-*.iso alpine-standard-*.iso.sha256 alpine-standard-*.iso.asc
alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso is the 3.20.3 version Standard image file in iso format for x86_64 architecture. Image file can also be gz for certain cases.
Verifying downloaded image
From Security point of view, verify the downloaded image file for both checksum and GPG signature before proceeding further. The three required utilities i.e sha256, curl and gpg or their equivalents are available in every operating system including Linux, windows, Mac and BSD derivaties.
The sha256 checksum verifies the integrity of the downloaded image i.e no modifications occurred during download.
sha256sum -c alpine-*.iso.sha256
The GPG signature verifies the link between the downloaded image to the individual who signed it. Signature verification involves two steps:
Step 1. Download and import the gpg signature from official website
curl https://alpinelinux.org/keys/ncopa.asc | gpg --import ;
Step 2. Verify that the image signature matches with the one downloded in Step 1.
gpg --verify alpine-*.iso.asc alpine-*.iso
Preparing installation media
All data currently on the installation media will be lost, when Alpine Linux installation image is written on it. Be extremely careful to correctly identify the device name for the installation media using the commands lsblk and blkid.
In Linux, dd command can write the downloaded image file to the installation media i.e target device.
# dd if=alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M status=progress; eject /dev/sdX
If your version of dd does not support the option "status=progress", remove it. The eject command removes the target device from the system and ensures the write cache is completely flushed.
In Windows, Rufus has been tested to create bootable USB flash drives and worked for Alpine Linux 3.12.x with the following settings:
- Partition scheme:
MBRTarget system:BIOS or UEFI - File system:
FAT32Cluster size:4096 bytes (default)
Verifying Installation media
After detaching and re-attaching the device, a bit-wise comparison can verify the data written to the device (instead of just data buffered in RAM). If the comparison terminates with an end-of-file error on the .iso file side, all the contents from the image have been written (and re-read) successfully:
# cmp ~/Downloads/alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso /dev/sdX cmp: EOF on alpine-standard-3.20.3-x86_64.iso
Booting Installation Media
Insert the Installation media to a proper drive or port of the computer and turn the machine on, or restart it, if already running.
If the computer does not automatically boot from the desired device, one needs to bring up the boot menu and choose the media to boot from. Depending on the computer, the menu may be accessed by repeatedly pressing a key quickly when booting starts. Some computers require that you press the button before starting the computer and hold it down while the computer boots. Typical keys are: F9-F12, sometimes F7 or F8. If these don't bring up the boot menu, it may be necessary to enter the BIOS configuration and adjust the boot settings, for which typical keys are: Del F1 F2 F6 or Esc.
Installation Step Details
Boot Process
The boot process of the alpine installation image first copies the entire operating system into the RAM memory, and then already starts a complete Alpine Linux system from there. It will initially only provide a basic command line environment that does not depend on reading from any (possibly slow) initial boot media, anymore.
Local log-in is possible as the user root. Initially, the root user has no password.
At the command prompt, an interactive script named setup-alpine is available to configure and install Alpine Linux. The script can be customized by the optional environment variables, in case of "data" or "sys" mode. For e.g USE_EFI=1 BOOTSIZE=512 setup-alpine, sets the disklabel type to gpt, creates 512MB /boot partition with vfat filesystem and uses grub as bootloader.
Base configuration
Launch the Alpine Linux Installation by running the setup-alpine script :
# setup-alpine
The question-and-answer dialog of setup-alpine takes care of the base configuration. It sets up a network connection to access Internet to configure the system to boot into one of three different Alpine Linux "disk" modes: "diskless"(none), "data" or "sys". If you choose to edit any option, the relevant file is opened in vi for editing.
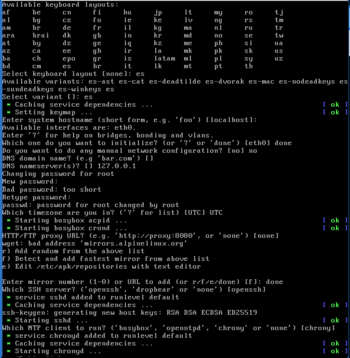
setup-alpine sessionThe setup-alpine script offers the following configuration options:
- Keyboard Layout (Local keyboard language and usage mode, e.g. us and variant of us-nodeadkeys.)
- Hostname (The name for the computer.)
- Network (Setup network connection to access Internet.)
- Available interfaces are: eth0 wlan0.(List depends on your hardware.)
- Which one do you want to initialize? (or '?' or 'done') [eth0] (Enter 'done' after configuring atleast one interface for Internet access.)
- Do you want to do any manual network configuration? (y/n) [n] (Default uses "DHCP".)
- DNS Servers (If none of the interfaces configured in previous step uses dhcp, set DNS server. If unsure, leave DNS domain name blank and using
9.9.9.9 2620:fe::fefor DNS is typically adequate.) - Root password (the password used to login to the root account)
- Timezone (Optionally display times/dates in your local time zone)
- HTTP/FTP Proxy (Proxy server to use for accessing the web/ftp. Use "none" for direct connections to websites and FTP servers.)
- Mirror (From where to download packages. Choose the organization you trust giving your usage patterns to.)
- Setup a user (Setting up a regular user account)
- NTP (Network Time Protocol client used for keeping the system clock in sync with a time server. Package "chrony" is part of the default install image.)
- SSH (Secure SHell remote access server. "OpenSSH" is part of the default install image. Use "none" to disable remote login, e.g. on laptops.)
- In most cases, either one of following line(s) is displayed as follows:
- No disks found. or Available disks are: sda (128.0 GB JMicron Tech )
- Disk Mode ( A pre-setup of the "diskless" system or base configuration is completed by answering "none" when asked for the following questions.)
- Which disk(s) would you like to use? (or '?' for help or 'none') none
- Enter where to store configs (/media/ or 'none') none
- The location of the package cache none
Base configuration is complete with the above step. Refer to the alternate courses of action to proceed further.
setup-alpine based System Disk Install
setup-alpine script based installation, needs an entire hard disk(s) for Alpine Linux and uses a partitioning layout with (/)root partition, /boot partition and a swap partition, where environment variables determine filesystem, size of the boot partition and the bootloader used. If your use case matches the above, at the final step of base configuration, type the appropriate hard disk device name instead of none. If multiple disks are chosen, RAID is used.
- At the Disk Mode stage, sda or relevant disk(s) must be chosen in the below screen:
- Which disk(s) would you like to use? (or '?' for help or 'none') sda
- Confirmation for the chosen disk(s) appears. The following disk is selected: sda (128.0 GB JMicron Tech ).

- How would you like to use it? ('sys', 'data', 'lvm' or '?' for help) sys
If sys is chosen, the setup-alpine script will complete the traditional hard-disk installation of Alpine Linux on the chosen disk(s) without further questions. Once the installation is complete, you can skip the next steps and proceed to reboot the system to boot into the newly installed Alpine Linux and configure further.
Custom partitioning
Manual partitioning of the harddisk may be needed to prepare the harddisk for "sys" mode install using setup-disk and for storing the config file using lbu commit and package cache for Diskless and for /var mount for Data disk mode installs. Refer Setting up disks manually page for specific configurations related to RAID, encryption, LVM, etc...
Preparing for the first boot
If System Disk Mode of installation was performed, ignore this section and proceed to reboot.
If the new local system was configured to run in "diskless" or "data" mode, and you do not want keep booting from the initial (and possibly read-only) installation media, create a customizable boot device. Once everything is in place, save your customized configuration with lbu commit before rebooting.
Reboot
First, remove the initial installation media from the boot drive, or detach it from the port it's connected to. The system may now be power-cycled or rebooted to confirm everything is working correctly. The relevant commands for this are poweroff or reboot. Login into the new system with the root account.
Completing the installation
The installation script installs only the base operating system. No applications e.g. web server, mail server, desktop environment, or web browsers are installed.
Please look at Post-Installation, for some common things to do after installation.
Custom Installation Instructions
Custom-made headless apkovl can be done by first booting the install media on some computer with a display and keyboard attached, or in a virtual machine, and doing an intermediate "diskless" setup of just the boot media (more details below), i.e. using the offical setup-alpine to configure the system's network, possibly for dhcp if needed, a ssh server, and a login user. Choosing "disks=none" for now, yet, configure to store configs on the boot media (if it is writable, otherwise on a separate storage media). And afterwards calling lbu commit to store the configs as local backup. Then your completed setup, including its securely created own private keys, will readily get (re)loaded on every subsequent (headless) boot from your custom-build <hostname>.apkovl.tar.gz stored on the boot media (or on an auxilary media or server location, in case the boot media is read-only).
- Bootstrap Alpine Linux on a headless system using pre-built
apkovloverlay file. - Kernels (kernel selection, e.g. for VMs or RPi)
- How to make a custom ISO image with mkimage (installation media with its own configuration)
- Directly booting an ISO file (without flashing it to a disk or device)
- Netboot Alpine Linux using iPXE
- Virtualization
Also see other Installation Category pages.
Post-Installation
Daily driver guide
Alpine Linux is built to be small and resource efficient. It is still a general purpose Linux distribution designed for power users. If you feel the defaults are too lightweight for desktop use, it is easy to get most of the regular stuff working and use it as a daily driver.
- Create a non-privileged user account for security reasons.
- Ensure that
communityrepository is enabled - Install graphics driver for your video hardware.
- Install a desktop using Setup-desktop script or manually install any desktop of your choice.
Basics
- Learn the alpine package keeper basics or refer wiki for more details.
- Install some fonts to make your desktop look better.
- Setup PipeWire to manage your audio, if setup-desktop did not install it for your already or you installed your desktop environment manually.
- Configure your Bluetooth, if you have one.
- Configure your printer.
- Enable documentation, so man pages are available.
- Secure your system by installing firewall software like awall or UFW.
- To keep your system secure, regularly check and apply updates with the package manager.
Advanced
- Use Flatpak to add packages that are not in the repositories.
- Install gcompat package to add a glibc compatability layer which lets you run glibc binaries as normal.
- Install a sandboxing application like AppArmor or Bubblewrap.
- Learn basics of openrc, the alpine Linux init system or refer Open rc wiki.
- If you want the rolling release version of Alpine Linux, enable the Edge repository.
- You may want to explore the testing repository, as it provides a lot more applications.
Other topics
Topics not strictly related to using Alpine Linux as desktop are listed below:
- Upgrade your OS, when a new version is released.
- Setting up Networking (including non-standard configurations)
- Init System (OpenRC) (configure a service to automatically boot at next reboot)
- Hosting services on Alpine (links to several mail/web/ssh server setup pages)
See also
- Tutorials and Howtos
- FAQs
- Comparison with other distros (how common things are done on Alpine)
- Wiki etiquette (to collaborate on this documentation)