Installation: Difference between revisions
(mv broader guides above general docs) |
m (→Broader Guides) |
||
| Line 297: | Line 297: | ||
=== Broader Guides === | === Broader Usage Guides === | ||
* See: [[Tutorials and Howtos]] | * See: [[Tutorials and Howtos]] | ||
= General Documentation = | = General Documentation = | ||
Revision as of 11:31, 24 June 2022

This page explains the basics to get started. But before actually installing, it can also help to skim through the Frequenty Asked Questions (FAQ).
If something isn't correct (anymore), or still incomplete, you will have to try figuring it out, or ask for the correct solution in the community.
And then carefully edit the wiki page.
Just as those before you did it for you.
Minimal Hardware Requirements
- At least 100 MB of RAM. [A graphical desktop system may require up to 1 GB minimum.]
- At least 0-700 MB space on a writable storage device. [Only required in "sys" or "data" mode installations (explained below). It is optional in "diskless" mode, where it may be used to save newer data and configurations states of a running system.]
For more information please check Requirements
Installation Overview
The general course of action
As usual, the regular installation procedure starts with three basic steps (additional details for all the steps follow below):
- Downloading and verifying the proper stable-release ISO installation image-file for the computer's architecture, and the corresponding
sha256(checksum) andGPG(signature) files. - Either burning the ISO image-file onto a blank CD/DVD/Blu-ray disk with disk burning software, or flashing the installation image onto a bootable storage device (USB-device, CF-/MMC-/SD-card, floppy, ...).
- Booting the computer from the prepared disk or storage device.
The boot process of the installation image first copies the entire operating system into the RAM memory, and then already starts a complete Alpine Linux system from there. It will initially only provide a basic command line environment that does not depend on reading from any (possibly slow) initial boot media, anymore.
Log-in is possible as the user root. Initially, the root user has no password.
At the command prompt, an interactive script named setup-alpine is available to configure and install the initial Alpine Linux system.
The question-and-answer dialog of setup-alpine takes care of the base configuration and allows to configure the system to
boot into one of three different Alpine Linux disk modes: "diskless", "data", or "sys".
These modes are explained in more detail in the following subsections.
setup-alpine and answering "none" when asked for the disk to use, and where to store configs, as well as for the location for the package cache.
Examples of preparation options:
- Preparing a custom partitioning or filesystem scheme that avoids to use and/or overwrite an entire disk (details below).
- Installing something that may be missing in the live system to configure the hardware, e.g. by using the alpine package manager
apk.
Examples of proceeding options:
setup-lbuto configure a "local backup" location for the diskless system, andlbu committo then save the local configuration state.setup-apkcacheto configure a local package cache storage location.setup-diskto add a "data" mode partition, or do a classic full install of the "diskless" system onto a "sys" disk or partition.
There are many more setup-scripts available. All these tools may also be run later to adjust specific configurations. For example, to set up a graphical environment as covered under Post-Install below.
Diskless Mode
This means the entire operating system with all applications are first loaded into RAM and then only run from there. This is the method used to boot for the .iso installation images. It's is extremely fast and can save on unnecessary disk spin-ups, power, and wear. It is similar to what other linux distributions may call a "frugal" install and boot into with a "toram" option. However, setup-alpine can also configure the installed system to boot like this if "disk=none" is specified.
Custom configurations and package selections may optionally still be preserved or "persist" across reboots by using the Alpine local backup tool lbu. It enables committing and reverting system states by using .apkovl files that are saved to writable storage and loaded when booting. If additional or updated packages have been added to the system, these may also be made available for automatic (re)installation during the boot phase without any (re)downloading, by enabling a local package cache on the writable storage.
[FIXME-1: Storing local configs and the package cache on an internal disk still requires some manual steps to have the partition listed, i.e. making a /etc/fstab entry, mountpoint, and mount, *before* running setup-alpine. The linked workaround also still requires to commit these configurations to disk manually before rebooting.]
If a writable partition is available, setup-alpine can be told to store the configs and the package cache on that writable partition. (Later, another directory on that same partition or another available partition may also be mounted as /home, or for example, for selected important applications to keep their run-time and user data on it.)
The boot device of the newly configured local "diskless" system may remain the initial (and possibly read-only) installation media. But it is also possible to copy the boot system to a partition (e.g. /dev/sdXY) with setup-bootable.
Data Disk Mode
This mode also runs from system RAM, thus it enjoys the same accelerated operation speed as "diskless" mode. However, swap storage and the entire /var directory tree get mounted from a persistent storage device (two newly created partitions). The directory /var holds e.g. all log files, mailspools, databases, etc., as well as lbu backup commits and the package cache. This mode is useful for having RAM accelerated servers with variable amounts of user-data that exceed the available RAM size. It enables the entire current system state (not just the boot state) to survive a system crash in accordance with the particular filesystem guarantees.
[FIXME-2]: Setup-alpine will create the data partition and mount it as /var, but can not yet configure lbu storage settings automatically. It is currently necessary to select "none" at the 'where to store configs' prompt (the new data partition is not listed) and configure lbu manually. For example, after running setup-alpine and before rebooting:
- Set LBU_MEDIA=sdXY in /etc/lbu/lbu.conf
- Execute a corresponding
echo "/dev/sdXY /media/sdXY <fstype> rw 0 0" >> /etc/fstab - Save the configuration for the next boot with
lbu commit.
In data disk mode, the boot device may also remain the initial (and possibly read-only) installation media, or be copied to a partition (e.g. /dev/sdXY) with setup-bootable.
System Disk Mode
This is a traditional hard-disk install.
If this mode is selected, the setup-alpine script creates three partitions on the selected storage device, /boot, swap and / (the filesystem root). This mode may, for example, be used for generic desktop and development machines.
For custom partitioning, see Setting_up_disks_manually.
To install along side another operating systems, see Installing_Alpine_on_HDD_dualbooting.
Basic Installation Step Details
|
This "Additional Details" section needs to be consolidated with the work at https://docs.alpinelinux.org (not finished) (Restructuring things there, moving and linking from here or there?).
Verifying the downloaded image-file
| OS type | SHA256 check |
SHA256 calculation (to be compared manually) |
GPG signature verification
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Linux | sha256sum -c alpine-*.iso.sha256 |
curl https://alpinelinux.org/keys/ncopa.asc | gpg --import ;
| |
| MACOS | - ? - | shasum -a 256 alpine-*.iso |
- ? - |
| OpenBSD | sha256 -C alpine-*.sha256 alpine-*.iso |
doas pkg_add gnupg;
| |
| FreeBSD | - ? - | /usr/local/bin/shasum -a 256 alpine-*.iso |
- ? - |
| NetBSD | - ? - | /usr/local/bin/shasum -a 256 alpine-*.iso |
- ? - |
| Windows (PowerShell installed) | - ? - | Get-FileHash .\alpine-<image-version>.iso -Algorithm SHA256 |
- ? - |
Flashing (direct data writing) the installation image-file onto a device or media
Unix/Linux
Under Unix (and thus Linux), "everything is a file" and the data in the image-file can be written to a device or media with the dd command. Afterward, executing the eject command removes the target device from the system and ensures the write cache is completely flushed.
dd if=<iso-file-to-read-in> of=<target-device-node-to-write-out-to> bs=4M oflag=sync status=progress; eject <target-device-node-to-write-to>
Be careful to correctly identify the target device as any data on it will be lost! All connected "bulk storage devices" can be listed with lsblk and blkid.
# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdX 0:0 0 64,0G 0 disk ├─sdX1 0:1 0 2G 0 part └─sdX2 0:2 0 30G 0 part /mnt/sdX2 # blkid /dev/sdX1: LABEL="some" UUID="..." TYPE="vfat" /dev/sdX2: LABEL="other" UUID="..." TYPE="ext4"
For example, if /dev/sdX is the desired target device, first make sure you un-mount all mounted partitions of the target device. For example sdX1 and sdX2:
umount /dev/sdX1 /dev/sdX2
For dd's output-file (of=), however, do not specify a partition number. For example, write to sdX, not sdX1:
Warning: This will overwrite the target device /dev/sdX, so before executing, make sure you have a backup of the data if you can't afford to lose it.
dd if=~/Downloads/alpine-standard-3.00.0-x86_64.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=4M oflag=sync status=progress; eject /dev/sdX
Windows
For example, there is the Rufus program. Rufus will enable you to create bootable USB flash drives under Windows.
Rufus has been tested and works for Alpine Linux 3.12.x with the following settings:
- Partition scheme:
MBR - Target system:
BIOS or UEFI - File system:
FAT32 - Cluster size:
4096 bytes (default)
Verifying the written installation media
After detaching and re-attaching the device, a bit-wise comparison can verify the data written to the device (instead of just data buffered in RAM). If the comparison terminates with an end-of-file error on the .iso file side, all the contents from the image have been written (and re-read) successfully:
# cmp ~/Downloads/alpine-standard-3.00.0-x86_64.iso /dev/sdX cmp: EOF on alpine-standard-3.00.0-x86_64.iso
Booting from external devices
Insert the boot media to a proper drive or port of the computer and turn the machine on, or restart it, if already running.
If the computer does not automatically boot from the desired device, one needs to bring up the boot menu and choose the media to boot from. Depending on the computer, the menu may be accessed by repeatedly pressing a key quickly when booting starts. Some computers require that you press the button before starting the computer and hold it down while the computer boots. Typical keys are: `F9`-`F12`, sometimes `F7` or `F8`. If these don't bring up the boot menu, it may be necessary to enter the BIOS configuration and adjust the boot settings, for which typical keys are: `Del.` `F1` `F2` `F6` or `Esc.`
Custom partitioning of the harddisk
It is possible to specify configurations for RAID, encryption, LVM, etc. as well as manual partitioning.
For "diskless" or "data disk" mode installs, manual partitioning may be needed to prepare the harddisk for committing local backups of the system state with lbu commit, to have a place for a package cache, or to use it for a /var mount.
For a "sys" install, custom partitioning is needed only if the desired scheme differs from overwriting an entire disk, or using the default set of a /boot, swap and root partition on the disk.
See Setting_up_disks_manually for the alpine options for RAID, encryption, LVM, etc. and manual partitioning.
Questions asked by setup-alpine
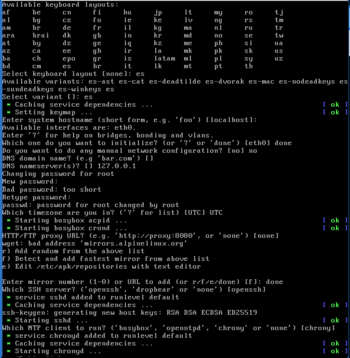
setup-alpine sessionThe setup-alpine script offers the following configuration options:
- Keyboard Layout (Local keyboard language and usage mode, e.g. us and variant of us-nodeadkeys.)
- Hostname (The name for the computer.)
- Network (For example, automatic IP address discovery with the "DHCP" protocol.)
- DNS Servers (Domain Name Servers to query. For privacy reasons it is NOT recommended to route every local request to servers like google's
8.8.8.8.) - Timezone
- Proxy (Proxy server to use for accessing the web. Use "none" for direct connections to the internet.)
- Mirror (From where to download packages. Choose the organization you trust giving your usage patterns to.)
- SSH (Secure SHell remote access server. "Openssh" is part of the default install image. Use "none" to disable remote login, e.g. on laptops.)
- NTP (Network Time Protocol client used for keeping the system clock in sync with a time server. Package "chrony" is part of the default install image.)
- Disk Mode (Select between diskless (disk="none"), "data" or "sys", as described above.)

Preparing for the first boot
If setup-alpine has finished configuring the "sys" disk mode, the system should be ready to reboot right away (see next subsection).
If the new local system was configured to run in "diskless" or "data" mode, and you do not want keep booting from the initial (and possibly read-only) installation media, the boot system needs to be copied to another device or partition.
The target partition may be identified using lsblk (after installing it with apk add lsblk) and/or blkid, similar to previously identifying the initial installation media device.
The procedure to copy the boot system is explained at setup-bootable
Once everything is in place, save your customized configuration with lbu commit before rebooting.
Rebooting and testing the new system
First, remove the initial installation media from the boot drive, or detach it fron the port it's connected to.
The system may now be power-cycled or rebooted to confirm everything is working correctly.
The relevant commands for this are poweroff or reboot.
Completing the installation
The installation script installs only the base operating system. No applications e.g. web server, mail server, desktop environment, or web browser are installed, and root is the only user.
Please look under "Post-Install" below, for some common things to do after installation.
Further Installation Instructions
Installation
- Kernels (kernel selection, e.g. for VMs or RPi)
- How to make a custom ISO image with mkimage (installation media with its own configuration)
- Directly booting an ISO file (without flashing it to a disk or device)
- Dual/multi-boot install to HDD partition
Post-Installation
- Setting up a new user (to allow remote, console, or graphical logins)
- Setting up Networking (including non-standard configurations)
- Package Management (apk) (how to search/add/del packages etc.)
- Upgrading Alpine (checking for and installing updates)
- Enable Community Repository (access to additional packages)
- man command/man pages
- Change default shell
- Running glibc programs (installation and development)
- Local backup utility
lbu(persisting RAM system configurations)- Back Up a Flash Memory Installation ("diskless mode" systems)
- Manually_editing_a_existing_apkovl (the stored custom configs)
- Init System (OpenRC) (configure a service to automatically boot at next reboot)
setup-xorg-base(setup graphical base environment)
- Hosting services on Alpine (links to several mail/web/ssh server setup pages)
- How to get regular stuff working (things one may miss in a too lightweight installation )
- Running applications and services in their own Firejail Security Sandbox
Also see other Installation Category pages.
Broader Usage Guides
- See: Tutorials and Howtos
General Documentation
For all Installations
- How to Contribute
- Developer Documentation
- Wiki etiquette (to collaborate on this documentation)
- Comparison with other distros (how common things are done on Alpine)
