Iwd: Difference between revisions
Prabuanand (talk | contribs) (updated instructions for ifupdown-ng configuration) |
Prabuanand (talk | contribs) (rearranged page and removed a hack related to Loss of connectivity due to changes in interface names) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:iwd}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:iwd}} | ||
iNet Wireless Daemon (iwd) project aims to provide a comprehensive Wi-Fi connectivity solution for Linux based devices. iwd provides a self-contained environment that only depends on the Linux Kernel and the runtime C library | iNet Wireless Daemon (iwd) project aims to provide a comprehensive Wi-Fi connectivity solution for Linux based devices. iwd provides a self-contained environment that only depends on the Linux Kernel and the runtime C library. | ||
{{Note|Alpine Linux supports both wireless daemons i.e [[Wi-Fi#wpa_supplicant|wpa_supplicant]] and [[iwd]]. Using both | {{Note|Alpine Linux supports both wireless daemons i.e [[Wi-Fi#wpa_supplicant|wpa_supplicant]] and [[iwd]]. Using both simultaneously leads to conflicts.}} | ||
== Prerequisites == | == Prerequisites == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
Install {{Pkg|iwd|arch=}} package using the command:{{Cmd|# apk add | Install {{Pkg|iwd|arch=}} package and {{Pkg|iwgtk|arch=}} package for the ''optional'' GUI utility [[#iwgtk|iwgtk]] using the command:{{Cmd|# apk add iwd iwgtk}} | ||
=== iwgtk === | |||
[[File:Iwgtk screenshot.png|thumb|right|100px|alt=iwgtk showing list of networks|iwgtk]] | |||
[https://github.com/J-Lentz/iwgtk iwgtk] is a wireless networking GUI utility for iwd with supported functionality similar to that of <code>iwctl</code>. Features include viewing and connecting to available networks, managing known networks, provisioning new networks via WPS or Wi-Fi Easy Connect, and an | |||
indicator (tray) icon displaying connection status and signal strength. | |||
== Network management mode == | |||
Next, choose one among the three modes listed below on how Network management will done with iwd before proceeding further. | |||
=== Standalone mode === | === Standalone mode === | ||
To have iwd do | To have iwd do all network management on its own upon connecting to a wi-fi network, requires {{pkg|openresolv|arch=}} package, so install it first:{{Cmd|# apk add {{Pkg|openresolv}}}} | ||
Then edit the configuration file {{path|/etc/iwd/main.conf}} and set it as follows: {{cat|/etc/iwd/main.conf|[General] | Then edit the configuration file {{path|/etc/iwd/main.conf}} and set it as follows: {{cat|/etc/iwd/main.conf|[General] | ||
EnableNetworkConfiguration{{=}}True | EnableNetworkConfiguration{{=}}True | ||
| Line 26: | Line 34: | ||
To test {{Pkg|openresolv}} package, issue the command:{{ic|# resolvconf -u}} to update the nameserver information in {{Path|/etc/resolv.conf}} file. | To test {{Pkg|openresolv}} package, issue the command:{{ic|# resolvconf -u}} to update the nameserver information in {{Path|/etc/resolv.conf}} file. | ||
=== | === iwd as a networkmanager backend === | ||
{{Main|NetworkManager#iwd_backend}} | {{Main|NetworkManager#iwd_backend}} | ||
[[NetworkManager]] can be | [[NetworkManager]] can be used for network management, with [[NetworkManager#iwd_backend|iwd configured as a wireless backend]]. | ||
=== | === iwd with ifupdown-ng === | ||
[[ifupdown-ng]] | iwd can delegate the responsibility dealing with IP address assignment (either static or DHCP) to [[ifupdown-ng]]. To do this edit the {{Path|/etc/network/interfaces}} file. For example, if you are using DHCP on the wlan0 interface: {{Cat|/etc/network/interfaces|auto lo | ||
iface lo inet loopback | |||
auto wlan0 | |||
iface wlan0 inet dhcp | |||
}} | |||
== Configuration == | == Configuration == | ||
=== Service configuration === | |||
{{ic|iwd}} service can be managed using standard [[OpenRC]] commands. Once iwd service has been fully configured and [[Configure_Networking#Connectivity_testing|tested]], then add the {{ic|iwd}} service and disable the {{ic|networking}} boot service:{{cmd|<nowiki># rc-update add iwd boot | |||
# rc-update del networking boot</nowiki>}} | |||
To proceed with the configuration of iwd, ensure that {{ic|wpa_supplicant}} service is stopped before starting iwd service:{{cmd|<nowiki># rc-service wpa_supplicant stop | |||
# rc-service iwd start</nowiki>}} | |||
=== Connection management === | |||
{{Tip|Basic connection management can be done in GUI using [[#iwgtk|'''iwgtk''']] utility.}} | |||
{{ic|iwctl}} tool can be run both in interactive and non-interactive mode. The non-interactive commands can be issued from the shell by suffixing {{ic|iwctl}} like {{ic|$ iwctl device list}} or {{ic|$ iwctl known-networks list}}. | |||
The example below shows the step-by-step procedure to configure iwd in an interactive mode. Begin by starting the {{ic|iwctl}} as follows:{{Cmd|$ iwctl}} | |||
The prompt should display: | |||
<span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># | |||
To list all available commands: | To list all available commands: | ||
<span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># help | <span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># help | ||
=== To connect to a network === | ==== To connect to a network ==== | ||
To list all Wi-Fi devices: | To list all Wi-Fi devices: | ||
| Line 75: | Line 101: | ||
* iwd only supports PSK pass-phrases from 8 to 63 ASCII-encoded characters. }} | * iwd only supports PSK pass-phrases from 8 to 63 ASCII-encoded characters. }} | ||
=== Disconnect from a network === | ==== Disconnect from a network ==== | ||
To disconnect from a network: | To disconnect from a network: | ||
| Line 81: | Line 107: | ||
<span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># station ''device'' disconnect | <span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># station ''device'' disconnect | ||
=== Show device and connection information === | ==== Show device and connection information ==== | ||
To display the details of a WiFi device, like MAC address: | To display the details of a WiFi device, like MAC address: | ||
| Line 91: | Line 117: | ||
<span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># station ''device'' show | <span style="color:green;">[iwd]</span># station ''device'' show | ||
=== Manage known networks === | ==== Manage known networks ==== | ||
To list networks you have connected to previously: | To list networks you have connected to previously: | ||
| Line 109: | Line 135: | ||
* time since the last connect.}} | * time since the last connect.}} | ||
== | == Troubleshooting == | ||
Resolve [[Wi-Fi#Troubleshooting|wireless driver issues]] first, if your wireless device is not detected, when the below command is issued:{{cmd|<nowiki>$ iwctl device list | |||
Devices | |||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
Name Address Powered Adapter Mode | |||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
wlan0 50:91:e3:71:83:d2 on phy0 station | |||
</nowiki>}} | |||
=== "The name net.connman.iwd was not provided by any .service files" === | |||
If {{ic|iwctl}} commands fail with the message {{ic|The name net.connman.iwd was not provided by any .service files Failed to retrieve IWD dbus objects, quitting...}}. | |||
The above error means that the {{ic|iwd}} daemon is not started. Start the [[#Service configuration|iwd daemon]] | |||
=== "ip: ioctl 0x8913 failed: No such device" === | |||
The above error message may occur whenever the networking service gets loaded by openrc after iwd. Refer to [[#Service configuration|Service configuration]] section. | |||
=== Loss of connectivity due to changes in interface names === | |||
Whenever system wakes up from sleep/suspend, the wireless interface name may change from {{ic|wlan0}} to {{ic|wlan1}}, {{ic|wlan2}} and so on resulting in loss of connectivity. If you expereince this issue, if [[eudev]] is used as device manager refer to [[eudev#Predictable network interface names|predictable network interface names]] section. | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Configure Networking|Main Networking page]] | * [[Configure Networking|Main Networking page]] | ||
* [[Wi-Fi|wpa_supplicant]] | * [[Wi-Fi|wpa_supplicant]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:23, 18 August 2025
iNet Wireless Daemon (iwd) project aims to provide a comprehensive Wi-Fi connectivity solution for Linux based devices. iwd provides a self-contained environment that only depends on the Linux Kernel and the runtime C library.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have working wireless drivers.
- iwd requires D-Bus service to be running.
Installation
Install iwd package and iwgtk package for the optional GUI utility iwgtk using the command:
# apk add iwd iwgtk
iwgtk
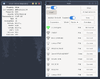
iwgtk is a wireless networking GUI utility for iwd with supported functionality similar to that of iwctl. Features include viewing and connecting to available networks, managing known networks, provisioning new networks via WPS or Wi-Fi Easy Connect, and an
indicator (tray) icon displaying connection status and signal strength.
Network management mode
Next, choose one among the three modes listed below on how Network management will done with iwd before proceeding further.
Standalone mode
To have iwd do all network management on its own upon connecting to a wi-fi network, requires openresolv package, so install it first:
# apk add openresolv
Then edit the configuration file /etc/iwd/main.conf and set it as follows:
Contents of /etc/iwd/main.conf
To test openresolv package, issue the command:# resolvconf -u to update the nameserver information in /etc/resolv.conf file.
iwd as a networkmanager backend
NetworkManager can be used for network management, with iwd configured as a wireless backend.
iwd with ifupdown-ng
iwd can delegate the responsibility dealing with IP address assignment (either static or DHCP) to ifupdown-ng. To do this edit the /etc/network/interfaces file. For example, if you are using DHCP on the wlan0 interface:
Contents of /etc/network/interfaces
Configuration
Service configuration
iwd service can be managed using standard OpenRC commands. Once iwd service has been fully configured and tested, then add the iwd service and disable the networking boot service:
# rc-update add iwd boot # rc-update del networking boot
To proceed with the configuration of iwd, ensure that wpa_supplicant service is stopped before starting iwd service:
# rc-service wpa_supplicant stop # rc-service iwd start
Connection management
iwctl tool can be run both in interactive and non-interactive mode. The non-interactive commands can be issued from the shell by suffixing iwctl like $ iwctl device list or $ iwctl known-networks list.
The example below shows the step-by-step procedure to configure iwd in an interactive mode. Begin by starting the iwctl as follows:
$ iwctl
The prompt should display:
[iwd]#
To list all available commands:
[iwd]# help
To connect to a network
To list all Wi-Fi devices:
[iwd]# device list
If your wireless adapter is not listed, refer to Wifi troubleshooting page.
If the device or its corresponding adapter is turned off, turn it on:
[iwd]# device device set-property Powered on
[iwd]# adapter adapter set-property Powered on
Then, to initiate a scan for networks (note that this command will not output anything):
[iwd]# station device scan
You can then list all available networks:
[iwd]# station device get-networks
Finally, to connect to a network:
[iwd]# station device connect SSID
If a passphrase is required, you will be prompted to enter it. Alternatively, you can supply it as a command line argument:
$ iwctl –passphrase passphrase station device connect SSID
- iwd automatically stores network passphrases in the /var/lib/iwd directory and uses them to auto-connect in the future.
- If you run diskless Alpine, be sure to commit:
# lbu add /var/lib/iwd && lbu commit -d
- To connect to a network with spaces in the SSID, the network name should be double quoted when connecting.
- iwd only supports PSK pass-phrases from 8 to 63 ASCII-encoded characters.
Disconnect from a network
To disconnect from a network:
[iwd]# station device disconnect
Show device and connection information
To display the details of a WiFi device, like MAC address:
[iwd]# device device show
To display the connection state, including the connected network of a Wi-Fi device:
[iwd]# station device show
Manage known networks
To list networks you have connected to previously:
[iwd]# known-networks list
To forget a known network:
[iwd]# known-networks SSID forget
- signal strength level
- security features
- maximum rate
- channel utilization
- time since the last connect.
Troubleshooting
Resolve wireless driver issues first, if your wireless device is not detected, when the below command is issued:
$ iwctl device list Devices -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Name Address Powered Adapter Mode -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- wlan0 50:91:e3:71:83:d2 on phy0 station
"The name net.connman.iwd was not provided by any .service files"
If iwctl commands fail with the message The name net.connman.iwd was not provided by any .service files Failed to retrieve IWD dbus objects, quitting....
The above error means that the iwd daemon is not started. Start the iwd daemon
"ip: ioctl 0x8913 failed: No such device"
The above error message may occur whenever the networking service gets loaded by openrc after iwd. Refer to Service configuration section.
Loss of connectivity due to changes in interface names
Whenever system wakes up from sleep/suspend, the wireless interface name may change from wlan0 to wlan1, wlan2 and so on resulting in loss of connectivity. If you expereince this issue, if eudev is used as device manager refer to predictable network interface names section.