How to build the Alpine Linux kernel: Difference between revisions
m (Added Category: Kernel) |
Prabuanand (talk | contribs) (updated wikilinks) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page quickly demonstrates building/compiling the default Alpine Linux [[Kernels|kernels]] "LTS" and "virt". They can be built within a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the speed of your system using <code>[[abuild]]</code>, [[aports]], and {{pkg|alpine-sdk}}. | |||
Alpine Linux supports multiple [[Kernels|kernels]] that vary in features, file sizes and architectures. [[Custom Kernel|Kernel customizations]] allow you to experiment by adding/removing kernel modules/features, is not covered in this page. | |||
== Before you start == | |||
A running instance of Alpine Linux and a non-root user with [https://pkgs.alpinelinux.org/package/edge/main/x86_64/doas doas] privileges (i.e. sudo, wheel group) are required to use <code>[[abuild]]</code>. | A running instance of Alpine Linux and a non-root user with [https://pkgs.alpinelinux.org/package/edge/main/x86_64/doas doas] privileges (i.e. sudo, wheel group) are required to use <code>[[abuild]]</code>. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 63: | ||
[[File:Alpine-kernel-revert.png|465px]] | [[File:Alpine-kernel-revert.png|465px]] | ||
== See | == See also == | ||
* [[Kernels]] | * [[Kernels]] | ||
* [[Custom Kernel|Custom Kernel (2018-present)]] | * [[Custom Kernel|Custom Kernel (2018-present)]] | ||
* [[Kernel_live_patching|Kernel Live Patching (KLP)]] | |||
[[Category:Kernel]] | [[Category:Kernel]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:19, 31 December 2025
This page quickly demonstrates building/compiling the default Alpine Linux kernels "LTS" and "virt". They can be built within a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the speed of your system using abuild, aports, and alpine-sdk.
Alpine Linux supports multiple kernels that vary in features, file sizes and architectures. Kernel customizations allow you to experiment by adding/removing kernel modules/features, is not covered in this page.
Before you start
A running instance of Alpine Linux and a non-root user with doas privileges (i.e. sudo, wheel group) are required to use abuild.
Build & install the kernel
Build
doas apk add alpine-sdk doas addgroup USERNAME abuild # your non-root user git clone --depth 1 https://gitlab.alpinelinux.org/alpine/aports.git abuild-keygen --append --install doas chmod a+r /etc/apk/keys/* # ensure new keys are readable cd aports/main/linux-lts/ time abuild -crK
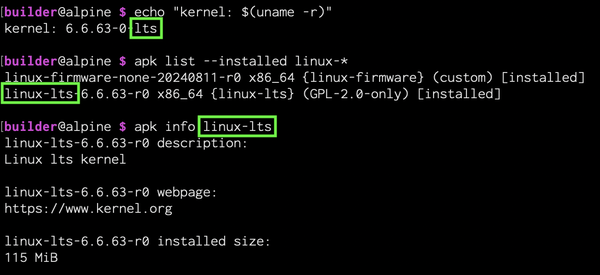
Identify backup
Identify the package name of your current kernel (e.g. linux-lts, linux-virt). This example shows that linux-lts is the current package that we would revert to as a backup.
echo "kernel: $(uname -r)" apk list --installed "linux-*"
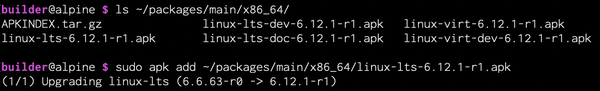
Install
Find the newly-built kernel file to install. This example shows how to install a newly-built x86_64 LTS kernel:
ls -r ~/packages/main/* doas apk add FILENAME doas reboot
After rebooting, verify the newly-installed kernel version:
echo "kernel: $(uname -r)"
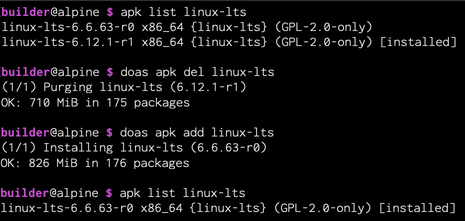
Revert
If needed, revert to the previous backup kernel package we identified earlier. This example shows how to revert to the previous "alpine-lts" package after removing the newly-installed "alpine-lts" (both are named "alpine-lts" yet refer to different versions/locations):
apk list linux-lts # newly-compiled kernel installed doas apk del linux-lts # newly-compiled kernel from file doas apk add linux-lts # previous kernel from Alpine repo apk list linux-lts # previous kernel installed doas reboot