Alpine Package Keeper
This page documents the Alpine Package Keeper(APK), the package manager in Alpine Linux. For a quickstart, refer Working with APK. Package management in Diskless mode requires additional steps involving Alpine Local Backup Utility (lbu) .
Overview
The apk-tools provides apk and it supports the following operations:
| add | Add new packages or upgrade packages to the running system |
| del | Delete packages from the running system |
| fix | Repair packages or system |
| update | Update the index of available packages |
| info | Prints information about installed or available packages |
| search | Search for packages or descriptions with wildcard patterns |
| upgrade | Upgrade the currently installed packages |
| cache | Maintenance operations for locally cached package repository |
| version | Compare version differences between installed and available packages |
| index | create a repository index from a list of packages |
| fetch | download (but not install) packages |
| audit | List changes to the file system from pristine package install state |
| verify | Verify a package signature |
| dot | Create a graphviz graph description for a given package |
| policy | Display the repository that updates a given package, plus repositories that also offer the package |
| stats | Display statistics, including number of packages installed and available, number of directories and files, etc. |
| manifest | Display checksums for files contained in a given package |
Packages and Repositories
Software packages for Alpine Linux are digitally signed tar.gz archives containing programs, configuration files, and dependency metadata. They have the extension .apk, and are often called "a-packs". Packages in Alpine Linux are organized into three official repositories. Technically, any directory with a collection of *.apk files with a special index file, named APKINDEX.tar.gz can be considered a repository, albeit a personal repository. Pinned Repositories can be used to holdback a specific version of a package.
World
At /etc/apk/world, apk maintains the world, that is, a list of constraints the package selection needs to fulfill. World describes the desired system state. The commands apk add foo and apk del bar manipulate the desired state by adding foo or bar as a dependency constraint in /etc/apk/world.
/etc/apk/world is a plaintext file with one constraint using dependency notation per line. Each line has the format:
name{@tag}{[<>~=]version}
Every constraint listed here must be solvable in order for the system to be considered correct, and no transaction may be committed that is incorrect. If it cannot verify the correctness of the requested change, it will back out adding the constraint before attempting to change what packages are actually installed on the system. Thus apk will never commit a change to the system that leaves it unbootable.
If /etc/apk/world is edited manually, run apk fix to synchronize the installed packages with the desired system state. Package installation or removal is done as a side effect of modifying this system state.
apk fix
Update Package list
Alpine Linux repositories change as packages are added and upgraded. To get the latest list of available packages, use the update command. The command downloads the APKINDEX.tar.gz from each repository and stores it in the local cache, typically /var/cache/apk/, /var/lib/apk/ or /etc/apk/cache/.
apk update
Adding the --update-cache, or for short -U switch to another apk command, as in apk --update-cache upgrade or apk -U add ..., the command has the same effect as first running apk update before the other apk command.
It is a good idea to always do an update right before doing an upgrade or add command. That way the command will install the latest available packages from the repositories.
Add a Package
Use add to install packages from a repository. Any necessary dependencies are also installed. If you have multiple repositories, the add command installs the newest package.
apk add openssh apk add openssh openntp vim
Packages from pinned repositories can be installed by adding tags to them.
apk add wireguard-go@testing
.
Add a local Package
To install a locally available apk package, for example if this device has no internet access but you can upload apk packages directly to it, use the --allow-untrusted flag:
apk add --allow-untrusted /path/to/file.apk
Note that multiple packages can be given. When installing a local package, all dependencies should also be specified. For example:
apk add --allow-untrusted /var/tig-2.2-r0.apk /var/git-2.11.1-20.apk
Remove a Package
Use del to remove a package (and dependencies that are no longer needed.)
apk del openssh apk del openssh openntp vim
Upgrade a Running System
To get the latest security upgrades and bugfixes available for the currently installed release branch of a running system, there are two steps:
- update the list of available packages
- upgrade the installed packages:
apk update apk upgrade
Or, combining the same into one single command:
apk -U upgrade
Here is an example, showing the procedure on a system that has repositories pinned:
# apk update fetch https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.6/main/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz fetch https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.6/community/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz fetch https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/edge/testing/x86_64/APKINDEX.tar.gz v3.6.2-191-gf98d79930f [https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.6/main] v3.6.2-190-ga5d68c47df [https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.6/community] v3.6.0-4624-g11f1b9c8ab [https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/edge/testing] OK: 20118 distinct packages available # apk upgrade (1/2) Upgrading extra-cmake-modules@testing (5.38.0-r0 -> 5.39.0-r0) (2/2) Upgrading extra-cmake-modules-doc@testing (5.38.0-r0 -> 5.39.0-r0) Executing mdocml-apropos-1.14.1-r0.trigger OK: 2635 MiB in 803 packages
To upgrade only specific packages, use the upgrade command and specify them:
apk update apk upgrade busybox
To enable unattended, automatic upgrades of packages, see the apk-autoupdate package. Refer Upgrading Alpine to upgrade Alpine Linux to a newer release branch.
Upgrading "diskless" and "data" disk mode installs
For upgrading diskless and Data disk mode installs, Upgrading a running system requires few extra steps.
Search for Packages
The search command searches the repository Index files for installable packages.
The return format is Package-Version. Omit Version for apk add Package
Examples:
- To list all packages available, along with their descriptions:
apk search -v
- To list all packages are part of the ACF system:
apk search -v 'acf*'
- To list all packages that list NTP as part of their description, use the -d or --description option:
apk search -v --description 'NTP'
Information on Packages
The info command provides information on the contents of packages, their dependencies, and which files belong to a package.
For a given package, each element can be chosen (for example, -w to show just the webpage information), or all information displayed with the -a command.
Example:
apk info -a zlib
zlib-1.2.5-r1 description: A compression/decompression Library zlib-1.2.5-r1 webpage: https://zlib.net zlib-1.2.5-r1 installed size: 94208 zlib-1.2.5-r1 depends on: libc0.9.32 zlib-1.2.5-r1 is required by: libcrypto1.0-1.0.0-r0 apk-tools-2.0.2-r4 openssh-client-5.4_p1-r2 openssh-5.4_p1-r2 libssl1.0-1.0.0-r0 freeswitch-1.0.6-r6 atop-1.25-r0 zlib-1.2.5-r1 contains: lib/libz.so.1.2.5 lib/libz.so.1 lib/libz.so zlib-1.2.5-r1 triggers:
As shown in the example you can determine
- The description of the package (-d or --description)
- The webpage where the application is hosted (-w or --webpage)
- The size the package will require once installed (in bytes) (-s or --size)
- What packages are required to use this one (depends) (-R or --depends)
- What packages require this one to be installed (required by) (-r or --rdepends)
- The contents of the package, that is, which files it installs (-L or --contents)
- Any triggers this package sets. (-t or --triggers) Listed here are directories that are watched; if a change happens to the directory, then the trigger script is run at the end of the apk add/delete. For example, doing a depmod once after installing all packages that add kernel modules.
Check file ownership
The info command is also useful to determine which package a file belongs to. For example:
apk info --who-owns /sbin/lbu
will display
/sbin/lbu is owned by alpine-conf-x.x-rx
Check Dependencies
The info command specific to check package dependency and reverse dependency is explained below:
The option -R or --depends lists the dependencies of the package.
apk info --depends pipewire
pipewire-1.0.6-r1 depends on: /bin/sh so:libc.musl-x86_64.so.1 so:libpipewire-0.3.so.0
The option -r or --rdepends lists the reverse dependencies of the package (all other packages which depend on the package).
apk info --rdepends pipewire
pipewire-1.0.6-r1 is required by: xdg-desktop-portal-wlr-0.7.1-r0 pipewire-pulse-1.0.6-r1
Listing installed packages
To list all installed packages, use:
apk info
To list all installed packages in alphabetical order, with a description of each, do:
apk -vv info
The apk tool does not have a subcommand to list manually-installed packages that do not have reverse dependencies. To get this information on a traditional system that is not using lbu, try this script. Note that this approach will also list core packages like alpine-base that should not be removed.
#!/bin/sh
apk info | grep -ve '-doc$' | sort | while read pkg
do
rdep=`apk info -qr "$pkg"`
[ -z "$rdep" ] && echo $pkg
done
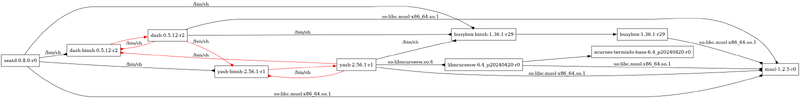
apk dot
The dot option renders package dependencies as graphviz graphs. Steps to use the dot option is documented below:
Save the output of apk dot option to a dot file.
$ apk dot seatd > seatd_dependencies.dot
Use Graphviz to convert the dot file into a graphical format such as PNG, PDF, or SVG.
$ dot -Tpng seatd_dependencies.dot -o seatd_dependencies.png
apk policy
To display the repository a package was installed from and will be updated from, plus any tagged or enabled repositories where it is also offered, if any, for this architecture - its policy:
apk policy package
For example:
$ apk policy vlc
vlc policy:
2.2.6-r1:
lib/apk/db/installed
https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.7/community
3.0.0_rc2-r1:
@edgecommunity https://dl-3.alpinelinux.org/alpine/edge/community
Local Cache
Overview
APK can keep a cache of installed packages on a local disk.
In diskless installations, since these packages are available during boot, packages can then be automatically (re-)installed from local media into RAM when booting, without requiring, and even before there is a network connection. The cache can be stored on any writable media, or at the same location as the .apkovl file from the local backup utility lbu.
HDD or sys mode installs don't need an apk cache to maintain their state, it still allows to serve packages over the network, though, e.g. to get installed by other local machines.
Enabling Local Cache
Execute the script setup-apkcache will assist in enabling a local cache. The script creates a symlink named /etc/apk/cache that points to the cache directory.
setup-apkcache
Cache can also be manually enabled by creating a cache dir and then symlink it to /etc/apk/cache:
mkdir -p /var/cache/apk ln -s /var/cache/apk /etc/apk/cache
On a diskless installation, to make the disk where the cache directory is present be automatically mounted at boot create an empty file .boot_repository inside the cache directory.
Cache maintenance
Removing older packages
When newer packages are added to the cache over time, the older versions of the packages default to remain in the cache directory.
The older versions of packages can be removed with the clean command.
apk cache clean
Or to see what is deleted include the verbose switch:
apk -v cache clean
Download missing packages
If you accidentally delete packages from the cache directory, you can make sure they are there with the download command,
apk cache download
Delete and download in one step
You can combine the two steps into one with the sync command - this cleans out old packages and downloads missing packages.
apk cache -v sync
Automatically Cleaning Cache on Reboot
To automatically attempt to validate your cache on reboot, you can add the above command to a /etc/local.d/*.stop file:
Contents of /etc/local.d/cache.stop
Local Cache on tmpfs volumes
In some circumstances it might be useful to have the cache reside on tmpfs, for example if you only wish for it to last as long as the system is up.
NOTE: apk is coded to ignore tmpfs caches, and this is correct behaviour in most instances. Using tmpfs as a package cache can consume large amounts of system memory if you install a lot of packages, possibly resulting in a crashed system. You can limit this by restricting the size of your cache to a small number (128M in the example below).
To do it, you need to create an image inside which your cache can live. We do this by creating an image file, formatting it with ext2, and mounting it at /etc/apk/cache.
apk add e2fsprogs dd if=/dev/zero of=/apkcache.img bs=1M count=128 mkfs.ext2 -F /apkcache.img mkdir -p /etc/apk/cache mount -t ext2 /apkcache.img /etc/apk/cache apk update
As usual, if you want to download currently installed packages into the cache, use apk cache sync.
Advanced APK Usage
Commandline repository options
By default, the apk utility will use the system repositories for all operations. This behavior can be overridden by the following options:
| --repositories-file REPOFILE | Override the system repositories by specifying a repositories file. |
| -X|--repository REPO | Specify a supplemental repository that will be used in addition to the system repositories. This option can be provided multiple times. |
apk add cherokee --update-cache --repository https://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/edge/testing/ --allow-untrusted
Holding a specific package back
In certain cases, you may want to upgrade a system, but keep a specific package at a back level. It is possible to add "sticky" or versioned dependencies. For instance, to hold the asterisk package to the 1.6.2 level or lower:
apk add asterisk=1.6.0.21-r0
or
apk add 'asterisk<1.6.1'
after which a
apk upgrade
will upgrade the entire system, keeping the asterisk package at the 1.6.0 or lower level
To later upgrade to the current version,
apk add 'asterisk>1.6.1'
will ensure that 1.6.1 is the minimum version used.
You can also use "fuzzy" version matching to pin the version to a major/minor release. For example:
apk add 'asterisk=~1.6'
will match any version of asterisk that starts with 1.6 (such as 1.6.0.21-r0 or 1.6.9.31-r9).
If you desire deterministic, repeatable package installation (such as with containerized environments) via package pinning, it is important to understand your package repo's version retention rules. Always pin to a package version that is intended for your release branch. Pinning to a version on the edge branch may stop working after the package version is revoked from the repo.
Commit hooks
If you'd like to trigger an action or run a certain script on every commit made by apk, there's a built-in method for that. On every commit apk looks for executables located in the "/etc/apk/commit_hooks.d/" directory, and executes them both before and after the commit. To provide some way to selectively run hooks either before or after a change is commited by apk, the scripts are called with "pre-commit" or "post-commit" as argument 1. This is an example of a hook to do different things before and after commit:
#!/bin/sh if [ "$1" = "pre-commit" ]; then do_something elif [ "$1" = "post-commit" ]; then do_something_else fi
Commit hooks are $PATH-aware, so for the sake of security it's recommended to specify absolute paths to executables.
Rosetta Stone
Rosetta Stone or a Comparison chart shows how standard things related to package management are done in Alpine Linux compared to other popular distributions.
Troubleshooting
ERROR: unable to select packages
This error typically indicates that the package manager cannot find a suitable package to install. On issuing a command to add a package for eg: apk add labwc, you may receive below error message:
ERROR: unable to select packages: labwc (no such package): required by: world[labwc]
The above error indicates labwc does not exist in the repositories currently configured in /etc/apk/repositories. Ensure that community repository is enabled, as by default only main repository is enabled. You may also want to check packages database to identify the correct package name and the repository in which the package is available.
ERROR: unsatisfiable constraints
This error signifies a dependency conflict. It means that the package you're trying to install has dependencies that cannot be simultaneously satisfied within the current package repository.
You may want to check packages database to identify the correct package name and version and the repository in which the package is available.
WARNING: This apk-tools is OLD!
apk update, apk upgrade or apk add may report the following:
WARNING: This apk-tools is OLD! Some packages might not function properly
This may happen if you are running Alpine Linux stable version with a certain edge/main, edge/community or testing package(s) also installed. One resolution is to consider upgrading apk-tools. If edge is already tagged in your repositories, then try:
apk add --upgrade apk-tools@edge
ERROR: UNTRUSTED signature
This happens when the release version changes. You need to update the local apk keys.
If you have already updated your repositories, allow them to update without the trusted key:
apk update --allow-untrusted
Then install the keys upgrade:
apk fix --upgrade --allow-untrusted alpine-keys
Now updates and upgrades should proceed normally.
Alternative, the updated alpine-keys package may be obtained, verified, installed directly, as covered earlier, prior to a repository update.
World updated but the following packages are not removed
On issuing a command to remove a package for eg: apk del btrfs-progs, you may receive below error message:
World updated, but the following packages are not removed due to: btrfs-progs: btrbk
Here, the removal of package btrfs-progs affects another package btrbk in the constraints file /etc/apk/world. So the package btrfs-progs will be removed from the constraints file, but not removed from the system. The btrfs-progs will remain in the system, until the constraint i.e btrbk which depends on btrfs-progs is removed.
If apk del btrbk is issued, the package btrfs-progs will be automatically removed from system as the constraint btrfs-progs does not exist in /etc/apk/world.
See Also
- Comparison with other distros
- Upgrading Alpine Linux to newer Release Branch
- Understand Repositories in Alpine Linux