Linux Router with VPN on a Raspberry Pi
Rationale
This guide demonstrates how to set up a Raspberry Pi as an open source Linux router with a VPN tunnel. You will need a USB ethernet adaptor. I chose the Apple USB Ethernet Adapter as it contains a ASIX AX88772 which has good Linux support. Be sure to not buy a cheap counterfeit one as they do exist. You may choose to also buy an RTC clock. If you don't have an RTC clock, the time is lost when your Pi is shut down. When it is rebooted, the time will be set back to Thursday, 1 January 1970. As this is earlier than the creation time of your VPN certificates OpenVPN will refuse to start, which may mean you cannot do DNS lookups over VPN.
For wireless, a separate access point was purchased (Ubiquiti UniFi AP) because it contains a Atheros AR9287 which is supported by ath9k and I was keen to avoid blob drivers.
You could choose to use an old x86/amd64 system instead. This may be a more attractive option if you want to route high speeds. If you want to route speeds above 100 Mbit/s you'll want to make use of hardware encryption like AES-NI.
The network in this tutorial looks like this:
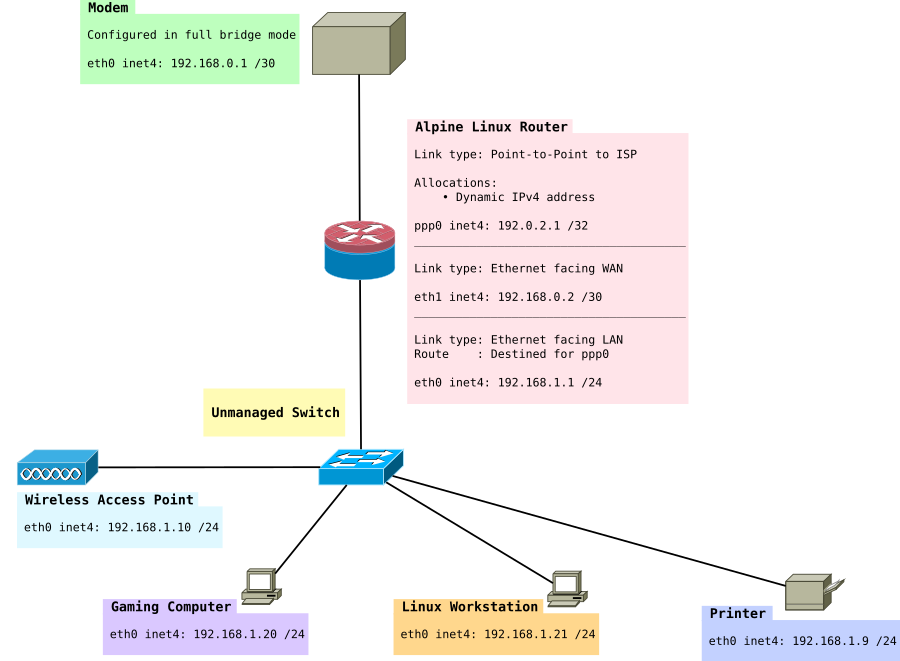
Installation
This guide assumes you're using Alpine Linux from a micro SD card in ramdisk mode. It assumes you've read the basics of how to use Alpine local backup. The Raspberry Pi article contains information on how to install Alpine Linux on a Raspberry Pi.
Modem in full bridge mode
This particular page uses an example where you have a modem that uses PPPoE. You will need to modify parts which do not apply to you.
In this example I have a modem which has been configured in full bridge mode. PPP sessions are initiated on the router.
The modem I am using is a Cisco 877 Integrated Services Router. It has no web interface and is controlled over SSH. More information can be found Configuring a Cisco 877 in full bridge mode.
Configuring PPP
Next up we need to configure our router to be able to dial a PPP connection with our modem.
apk add ppp-pppoe
Check that the interface between your router and modem is eth1, or change it. Enter your credentials at the bottom of the file or use /etc/ppp/chap-secrets
/etc/ppp/peers/yourISP
# # PPP Configuration file # nolog # Try to get the IP address from the ISP noipdefault # Try to get the name server addresses from the ISP usepeerdns # Use this connection as the default route. defaultroute defaultroute-metric 300 # detatch after ppp0 interface is created updetach # Replace previous default route # This requires a special patch to ppp # https://sources.debian.net/src/ppp/2.4.7-1%2B1~exp1/debian/patches/cifdefroute.dif/ # replacedefaultroute # rp-pppoe plug-in makes PPPoE connection so rp-pppoe package is not needed # Possibly, you may need to change interface according your configuration plugin rp-pppoe.so eth1 # Uncomment if you need on-demand connection #demand # Disconnect after 300 seconds (5 minutes) of idle time. #idle 300 # Hide password from log entries hide-password # Send echo requests lcp-echo-interval 20 lcp-echo-failure 3 # Do not authenticate ISP peer noauth # Control connection consistency persist maxfail 0 # Control MTU size if your ISP does not force it #mtu 1492 user "username@yourISP.tld" # Compression bsdcomp 15 deflate 15
/etc/ppp/chap-secrets
Enter in your login credentials
# Secrets for authentication using CHAP # client server secret IP addresses "username@yourISP.tld" * "<your password>"
/etc/modules
Update modules to include pppoe:
pppoe
Network
/etc/hostname
Set this to your hostname eg:
<HOST_NAME>
/etc/hosts
Set your host and hostname
127.0.0.1 <HOST_NAME> <HOST_NAME>.<DOMAIN_NAME> ::1 <HOST_NAME> ipv6-gateway ipv6-loopback ff00::0 ipv6-localnet ff00::0 ipv6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ipv6-allnodes ff02::2 ipv6-allrouters ff02::3 ipv6-allhosts
/etc/network/interfaces
Configure your network interfaces:
# # Network Interfaces # auto lo auto eth0 auto eth1 # Loopback interfaces iface lo inet loopback address 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 # Internal Interface - facing LAN iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 # External Interface - facing Modem iface eth1 inet static address 192.168.0.2 netmask 255.255.255.252 broadcast 192.168.0.3 # Internet Connection iface ppp0 inet ppp pre-up /sbin/ip link set eth1 up provider <yourISP> # Make sure this is the same as /etc/ppp/peers/yourISP
Basic IPtables firewall with routing
This demonstrates how to set up basic routing with a permissive outgoing firewall. Incoming packets are blocked. The rest is commented in the rule set.
First install iptables:
apk add iptables ip6tables
######################################################################### # Basic iptables IPv4 routing rule set # # 192.168.1.0/24 routed directly to PPP0 via NAT # ######################################################################### # # Mangle Table # We leave this empty for the moment. # *mangle :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] COMMIT # # Filter Table # This is where we decide to ACCEPT, DROP or REJECT things # *filter :INPUT DROP [0:0] :FORWARD DROP [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] *filter # Create rule chain per input interface for forwarding packets :FWD_ETH0 - [0:0] :FWD_ETH1 - [0:0] :FWD_PPP0 - [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for input packets (for host itself) :IN_ETH0 - [0:0] :IN_ETH1 - [0:0] :IN_PPP0 - [0:0] # Create a log drop chain :LOG_DROP - [0:0] # Pass input packet to corresponding rule chain -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -j IN_ETH0 -A INPUT -i eth1 -j IN_ETH1 -A INPUT -i ppp0 -j IN_PPP0 # Pass forwarded packet to corresponding rule chain -A FORWARD -i eth0 -j FWD_ETH0 -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j FWD_ETH1 -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -j FWD_PPP0 # Forward LAN traffic out -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward SSH packets from network to modem -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.0/30 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward HTTP to modem's webserver -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.0/30 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward traffic to ISP -A FWD_PPP0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # SSH to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # DNS to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # FreeRadius Client (eg a UniFi AP) -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # NTP to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept traffic -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # SSH To Modem from Router -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # HTTP to modem -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept incoming tracked PPP0 connection -A IN_PPP0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT COMMIT # # NAT Table # This is where translation of packets happens and "forwarding" of ports # to specific hosts. # *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Port forwarding for Bittorrent -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.20 -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -p udp -m udp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.1.20 # Allows routing to our modem subnet so we can access the web interface or SSH -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j MASQUERADE # Allows hosts of the network to use the PPP tunnel -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT
I'd also highly suggest reading these resources if you are new to iptables:
- Frozen Tux Iptables-tutorial
- Words of wisdom for #netfilter
- Things You Should Know About Netfilter
- Towards the perfect ruleset
/etc/sysctl.conf
These sysctl settings harden a few things and were mostly borrowed from the ArchLinux wiki. This particular config was based on Kernel Sysctl Configuration for Linux from lisenet.
# https://www.lisenet.com/2015/kernel-sysctl-configuration-for-linux/ # Kernel sysctl configuration file for Linux # # By: www.lisenet.com # # Tested on a Red Hat server with physical memory of 2GB # # For binary values, 0 is disabled, 1 is enabled. See sysctl(8) and # sysctl.conf(5) for more details. # # References # https://www.suse.com/documentation/sles-12/book_hardening/data/sec_sec_prot_general_kernel.html # https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Sysctl # https://rtcamp.com/tutorials/linux/sysctl-conf/ # http://seriousbirder.com/blogs/centos-6-setting-shmmax-and-shmall-kernel-paramaters/ # http://kaivanov.blogspot.co.uk/2010/09/linux-tcp-tuning.html # Any process which has changed privilege levels # or is execute only will not be dumped (default) fs.suid_dumpable = 0 # File handle limit fs.file-max = 6577347 ######################################## ### Memory Tuning ### ######################################## # Use swap file when RAM usage is around 40 percent vm.swappiness = 60 # Controls the maximum number of shared memory segments, in pages (not bytes) # It is almost always 4K which is the recommended size # To be safe, run the following command: # getconf PAGE_SIZE => 4096 # Allocating 1GB below (1*1024*1024*1024/4096=262144) kernel.shmall = 262144 # Control the maximum size of a single shared memory segment, in bytes # Setting to half (1GB) of our physical memory kernel.shmmax = 1073741824 ######################################## ### Kernel Hardening ### ######################################## # Reboot a system after 10 seconds of kernel panic kernel.panic = 10 # Controls the System Request debugging functionality of the kernel kernel.sysrq = 0 # Controls whether core dumps will append the PID to the core filename. # Useful for debugging multi-threaded applications. kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 # Restricting access to kernel logs kernel.dmesg_restrict = 1 # If you're compiling your own kernel, then # this can help mitigating local root exploits kernel.kptr_restrict = 1 # Controls the default maxmimum size of a mesage queue # kernel.msgmnb = 65536 # Controls the maximum size of a message, in bytes # kernel.msgmax = 65536 # Enable ExecShield protection kernel.exec-shield = 1 # Enable by default, except if the application bits are set to "disable" kernel.randomize_va_space = 2 # Default kernel.pid_max = 32768 # Increase the length of the processor input queue net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 5000 # The maximum number of "backlogged sockets". Default net.core.somaxconn = 128 # Disable netfilter on bridges. #net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 0 #net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 0 #net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 0 ######################################## ### TCP/IP Stack Hardening ### ######################################## # Controls IP packet forwarding net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 # Disable fast recycling of TIME_WAIT sockets net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0 # Do not allow reuse of sockets in TIME_WAIT state for new connections net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 0 # Help prevent against SYN flood attacks net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 # If set to 0, protect against wrapping sequence numbers # Turning off timestamps may do more harm than good net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1 # Enable windows scaling net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1 # Maximum receive and send window size 16MB net.core.rmem_max = 16777216 net.core.wmem_max = 16777216 # Increase the read-buffer and write-buffer space allocatable # Autotuning TCP buffer limit 16MB net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 16777216 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 16777216 # Do not accept source routing net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0 # Disable redirects, not a router net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.secure_redirects = 0 # Enable source validation by reversed path # Protects from attackers that are using ip spoofing methods to do harm net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 2 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 2 # Log packets with impossible addresses to kernel log net.ipv4.conf.all.log_martians = 0 # Disabled to avoid spam net.ipv4.conf.default.log_martians = 0 # Disabled to avoid spam # Ignore all ECHO broadcast requests # Prevent being part of smurf attacks net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts = 1 # Ignore bogus ICMP errors net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1 net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_messages = 1 # Allowed local port range net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65535 # The minimum time sockets will stay in TIME_WAIT state net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 60 # protect against tcp time-wait assassination hazards # drop RST packets for sockets in the time-wait state # (not widely supported outside of linux, but conforms to RFC) net.ipv4.tcp_rfc1337 = 1 ######################################## ### IPv6 ### ######################################## # Disable IPv6 net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
DHCP
apk add dhcp
/etc/conf.d/dhcpd
Specify the configuration file location, interface to run on and that you want DHCPD to run in IPv4 mode.
# /etc/conf.d/dhcpd: config file for /etc/init.d/dhcpd # If you require more than one instance of dhcpd you can create symbolic # links to dhcpd service like so # cd /etc/init.d # ln -s dhcpd dhcpd.foo # cd ../conf.d # cp dhcpd dhcpd.foo # Now you can edit dhcpd.foo and specify a different configuration file. # You'll also need to specify a pidfile in that dhcpd.conf file. # See the pid-file-name option in the dhcpd.conf man page for details. # If you wish to run dhcpd in a chroot, uncomment the following line # DHCPD_CHROOT="/var/lib/dhcp/chroot" # All file paths below are relative to the chroot. # You can specify a different chroot directory but MAKE SURE it's empty. # Specify a configuration file - the default is /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf DHCPD_CONF="/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf" # Configure which interface or interfaces to for dhcpd to listen on. # List all interfaces space separated. If this is not specified then # we listen on all interfaces. DHCPD_IFACE="eth0" # Insert any other dhcpd options - see the man page for a full list. DHCPD_OPTS="-4"
/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
Configure your DHCP configuration server. For my DHCP server I'm going to have three subnets. Each has a specific purpose. You may choose to have any number of subnets like below. The broadcast-address would be different if you used VLANs. However in this case we are not.
authoritative;
ddns-update-style interim;
shared-network home {
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.240;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255;
option routers 192.168.1.1;
option ntp-servers 192.168.1.1;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.1;
allow unknown-clients;
}
subnet 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.2.10 192.168.2.240;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.2.255;
option routers 192.168.2.1;
option ntp-servers 192.168.2.1;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.1;
ignore unknown-clients;
}
subnet 192.168.3.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.3.10 192.168.3.240;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.3.255;
option routers 192.168.3.1;
option ntp-servers 192.168.3.1;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.1.1;
ignore unknown-clients;
}
}
host Gaming_Computer {
hardware ethernet 00:53:00:FF:FF:11;
fixed-address 192.168.1.20;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255;
option routers 192.168.1.1;
option host-name "gaming_computer";
}
host Linux_Workstation {
hardware ethernet 00:53:00:FF:FF:22;
fixed-address 192.168.2.21;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.2.255;
option routers 192.168.2.1;
option host-name "linux_workstation";
}
host printer {
hardware ethernet 00:53:00:FF:FF:33;
fixed-address 192.168.3.9;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option broadcast-address 192.168.3.255;
option routers 192.168.3.1;
}
Make sure to add this to the default run level once configured:
rc-update add dhcp default
Synchronizing the clock
You can choose to use BusyBox's ntpd or you can choose a more fully fledged option like OpenNTPD
Busybox /etc/conf.d/ntpd
Allow clients to synchronize their clocks with the router.
# By default ntpd runs as a client. Add -l to run as a server on port 123. NTPD_OPTS="-l -N -p <REMOTE TIME SERVER>"
Make sure to add this to the default run level once configured:
rc-update add ntpd default
Or if you prefer to synchronize with multiple servers...
OpenNTPD /etc/ntpd.conf
Install OpenNTPD
apk add openntpd
Add to default run level.
rc-update add openntpd default
/etc/ntpd.conf
# sample ntpd configuration file, see ntpd.conf(5) # Addresses to listen on (ntpd does not listen by default) listen on 192.168.1.1 listen on 192.168.2.1 # sync to a single server #server ntp.example.org # use a random selection of NTP Pool Time Servers # see http://support.ntp.org/bin/view/Servers/NTPPoolServers server 0.pool.ntp.org server 1.pool.ntp.org server 2.pool.ntp.org server 3.pool.ntp.org
tlsdate
The time can also be extracted from a https handshake. If the certificate is self-signed you will need to use skip-verification:
apk add tlsdate
tlsdate -V --skip-verification -p 80 -H example.com
timezone
You might also want to set a timezone, see Setting the timezone.
Saving Time
There are two ways to do this. If you didn't buy an RTC clock see Saving time with Software Clock. If you did like the PiFace Real Time Clock see Saving time with Hardware Clock
Unbound DNS forwarder with dnscrypt
We want to be able to do our lookups using dnscrypt without installing dnscrypt on every client on the network. Therefore the router will also run a DNS forwarder and request unknown domains over dnscrypt for our clients.
Unbound
First install
apk add unbound
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf
# unbound.conf(5) man page.
#
# See /usr/share/doc/unbound/examples/unbound.conf for a commented
# reference config file.
server:
# The following line will configure unbound to perform cryptographic
# DNSSEC validation using the root trust anchor.
# auto-trust-anchor-file: "/var/lib/unbound/root.key"
server:
verbosity: 1
num-threads: 4
interface: 192.168.1.1
do-ip4: yes
do-udp: yes
do-tcp: yes
access-control: 192.168.1.0/24 allow # Specify the subnets you want to listen on
access-control: 192.168.2.0/24 allow
do-not-query-localhost: no
chroot: ""
logfile: "/var/log/unbound.log"
use-syslog: no
hide-identity: yes
hide-version: yes
harden-glue: yes
harden-dnssec-stripped: yes
use-caps-for-id: yes
private-domain: "<HOSTNAME>"
#local-zone: "localhost." static
#local-data: "freebox.localhost. IN A 192.168.0.254"
#local-data-ptr: "192.168.0.254 freebox.localhost"
python:
remote-control:
forward-zone:
name: "."
forward-addr: 127.0.0.2@53
/etc/network/interfaces
You'll need a second loopback device, put it under the already existing one. Remember to add auto lo:1 to the top to bring it up on boot.
# # Network Interfaces # auto lo auto eth0 auto eth1 auto lo:1 # Loopback interfaces iface lo inet loopback address 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 iface lo:1 inet static address 127.0.0.2 netmask 255.0.0.0
Blocking nasties on the network by domain
It seems Microsoft has added a whole bunch of telemetry (spyware) analytics to Windows itself, whereby the OS now calls home with various information regarding it's usage. Back porting to previous versions of Windows is not an option, because the telemetry patches have also been back ported to 7/8.1.
Changing the knobs in Windows to stop this activity doesn't silence it completely, and they can always be reset with another update from Microsoft. It is however unlikely they will change the domains that are looked up. More information about that can be found here. You should also consider ditching Windows entirely and using a proper operating system that does not contain intrusive malware here are a few choices to consider.
As this is a network router, it might be prudent to block those domains.
This script takes in a list of domains and produces a filter file. We are directing all lookups to "0.0.0.1" which is an invalid IP and should fail immediately, unlike localhost. There are lists of the addresses in various places such as here and in this script.
You could also use this to block advertising, but that's probably easier to do in a web browser with something like UBlock/UBlock Origin.
/etc/unbound/unbound.conf
In your main unbound configuration add
include: /etc/unbound/filter.conf
Script to prepare/sort domains for Unbound
#!/bin/sh
##################################################
# Script taken from http://npr.me.uk/unbound.html
# Note you need GNU sed
##################################################
# Remove "#" comments
# Remove space and tab
# Remove blank lines
# Remove localhost and broadcasthost lines
# Keep just the hosts
# Remove leading and trailing space and tab (again)
# Make everything lower case
sed -e "s/#.*//" \
-e "s/[ \x09]*$//"\
-e "/^$/ d" \
-e "/^.*local.*/ d" \
-e "/^.*broadcasthost.*/ d" \
-e "s/\(^.*\) \([a-zA-Z0-9\.\-]*\)/\2/" \
-e "s/^[ \x09]*//;s/[ \x09]*$//" $1 \
-e "s/\(.*\)/\L\1/" hosts.txt > temp1.txt
# Remove any duplicate hosts
sort temp1.txt | uniq >temp2.txt
# Remove any hosts starting with "."
# Create the two required lines for each host.
sed -e "/^\..*/ d" \
-e "s/\(^.*\)/local-zone: \x22\1\x22 redirect\nlocal-data: \x22\1 A 0.0.0.1\x22/" \
temp2.txt > filter.conf
# Clean up
rm temp1.txt
rm temp2.txt
/etc/unbound/filter.conf
local-zone: "a-0001.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0001.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0002.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0002.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0003.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0003.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0004.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0004.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0005.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0005.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0006.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0006.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0007.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0007.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0008.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0008.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-0009.a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-0009.a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a-msedge.net" redirect local-data: "a-msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a.ads1.msn.com" redirect local-data: "a.ads1.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a.ads2.msads.net" redirect local-data: "a.ads2.msads.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a.ads2.msn.com" redirect local-data: "a.ads2.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "a.rad.msn.com" redirect local-data: "a.rad.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ac3.msn.com" redirect local-data: "ac3.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ad.doubleclick.net" redirect local-data: "ad.doubleclick.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "adnexus.net" redirect local-data: "adnexus.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "adnxs.com" redirect local-data: "adnxs.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ads.msn.com" redirect local-data: "ads.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ads1.msads.net" redirect local-data: "ads1.msads.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ads1.msn.com" redirect local-data: "ads1.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "aidps.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "aidps.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "aka-cdn-ns.adtech.de" redirect local-data: "aka-cdn-ns.adtech.de A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "apps.skype.com" redirect local-data: "apps.skype.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "az361816.vo.msecnd.net" redirect local-data: "az361816.vo.msecnd.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "az512334.vo.msecnd.net" redirect local-data: "az512334.vo.msecnd.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "b.ads1.msn.com" redirect local-data: "b.ads1.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "b.ads2.msads.net" redirect local-data: "b.ads2.msads.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "b.rad.msn.com" redirect local-data: "b.rad.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "bs.serving-sys.com" redirect local-data: "bs.serving-sys.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "c.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "c.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "c.msn.com" redirect local-data: "c.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "cdn.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "cdn.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "cds26.ams9.msecn.net" redirect local-data: "cds26.ams9.msecn.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "choice.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "choice.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "choice.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "choice.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "compatexchange.cloudapp.net" redirect local-data: "compatexchange.cloudapp.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "corp.sts.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "corp.sts.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "corpext.msitadfs.glbdns2.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "corpext.msitadfs.glbdns2.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "cs1.wpc.v0cdn.net" redirect local-data: "cs1.wpc.v0cdn.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "db3aqu.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "db3aqu.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "df.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "df.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "diagnostics.support.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "diagnostics.support.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ec.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "ec.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "fe2.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net" redirect local-data: "fe2.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "feedback.microsoft-hohm.com" redirect local-data: "feedback.microsoft-hohm.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "feedback.search.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "feedback.search.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "feedback.windows.com" redirect local-data: "feedback.windows.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "flex.msn.com" redirect local-data: "flex.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "g.msn.com" redirect local-data: "g.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "h1.msn.com" redirect local-data: "h1.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "h2.msn.com" redirect local-data: "h2.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "i1.services.social.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "i1.services.social.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "i1.services.social.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "i1.services.social.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "lb1.www.ms.akadns.net" redirect local-data: "lb1.www.ms.akadns.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "live.rads.msn.com" redirect local-data: "live.rads.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "m.adnxs.com" redirect local-data: "m.adnxs.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "m.hotmail.com" redirect local-data: "m.hotmail.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "msedge.net" redirect local-data: "msedge.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "msftncsi.com" redirect local-data: "msftncsi.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "msnbot-65-55-108-23.search.msn.com" redirect local-data: "msnbot-65-55-108-23.search.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "msntest.serving-sys.com" redirect local-data: "msntest.serving-sys.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "oca.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "oca.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "oca.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "oca.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "pre.footprintpredict.com" redirect local-data: "pre.footprintpredict.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "preview.msn.com" redirect local-data: "preview.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "pricelist.skype.com" redirect local-data: "pricelist.skype.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "rad.live.com" redirect local-data: "rad.live.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "rad.msn.com" redirect local-data: "rad.msn.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "redir.metaservices.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "redir.metaservices.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "reports.wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "reports.wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "s.gateway.messenger.live.com" redirect local-data: "s.gateway.messenger.live.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "s0.2mdn.net" redirect local-data: "s0.2mdn.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "schemas.microsoft.akadns.net" redirect local-data: "schemas.microsoft.akadns.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "secure.adnxs.com" redirect local-data: "secure.adnxs.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "secure.flashtalking.com" redirect local-data: "secure.flashtalking.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "services.wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "services.wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "settings-sandbox.data.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "settings-sandbox.data.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "settings-win.data.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "settings-win.data.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "sls.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net" redirect local-data: "sls.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "so.2mdn.net" redirect local-data: "so.2mdn.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "sqm.df.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "sqm.df.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "sqm.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "sqm.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "sqm.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "sqm.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "static.2mdn.net" redirect local-data: "static.2mdn.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "statsfe1.ws.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "statsfe1.ws.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "statsfe2.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net" redirect local-data: "statsfe2.update.microsoft.com.akadns.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "statsfe2.ws.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "statsfe2.ws.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "survey.watson.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "survey.watson.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telecommand.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "telecommand.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telecommand.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "telecommand.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telemetry.appex.bing.net" redirect local-data: "telemetry.appex.bing.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telemetry.appex.bing.net:443" redirect local-data: "telemetry.appex.bing.net:443 A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "telemetry.urs.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "telemetry.urs.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "ui.skype.com" redirect local-data: "ui.skype.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "view.atdmt.com" redirect local-data: "view.atdmt.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "vortex-bn2.metron.live.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "vortex-bn2.metron.live.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "vortex-cy2.metron.live.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "vortex-cy2.metron.live.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "vortex-sandbox.data.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "vortex-sandbox.data.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "vortex-win.data.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "vortex-win.data.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "vortex.data.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "vortex.data.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "watson.live.com" redirect local-data: "watson.live.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "watson.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "watson.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "watson.ppe.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "watson.ppe.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "watson.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "watson.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "watson.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net" redirect local-data: "watson.telemetry.microsoft.com.nsatc.net A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com" redirect local-data: "wes.df.telemetry.microsoft.com A 0.0.0.1" local-zone: "www.msftncsi.com" redirect local-data: "www.msftncsi.com A 0.0.0.1"
DNSCrypt
You'll need to pin the testing repository. See: Alpine Linux package management#Repository pinning
Then install:
apk add dnscrypt-proxy@testing
/etc/conf.d/dnscrypt-proxy
Enter a dnscrypt server, it should look something like this:
# DNSCRYPT_LOGFILE=/var/log/dnscrypt-proxy/dnscrypt-proxy.log # override listen address where DNSCRYPT listen DNSCRYPT_LOCALIP=127.0.0.2:53 RESOLVER=208.67.220.220:443 PROVIDER=2.dnscrypt-cert.opendns.com PUBKEY=B735:1140:206F:225D:3E2B:D822:D7FD:691E:A1C3:3CC8:D666:8D0C:BE04:BFAB:CA43:FB79
Finally add both to the default run level
rc-update add unbound default
rc-update add dnscrypt-proxy default
WiFi 802.1x EAP and FreeRadius
A more secure way than using pre-shared keys (WPA2) is to use EAP-TLS and use separate certificates for each device. See FreeRadius EAP-TLS configuration
VPN Tunnel on specific subnet
As mentioned earlier in this article it might be useful to have a VPN subnet and a non-VPN subnet. Typically gaming consoles or computers might want low-latency connections. For this exercise we use fwmark.
We expand the network to look like this:
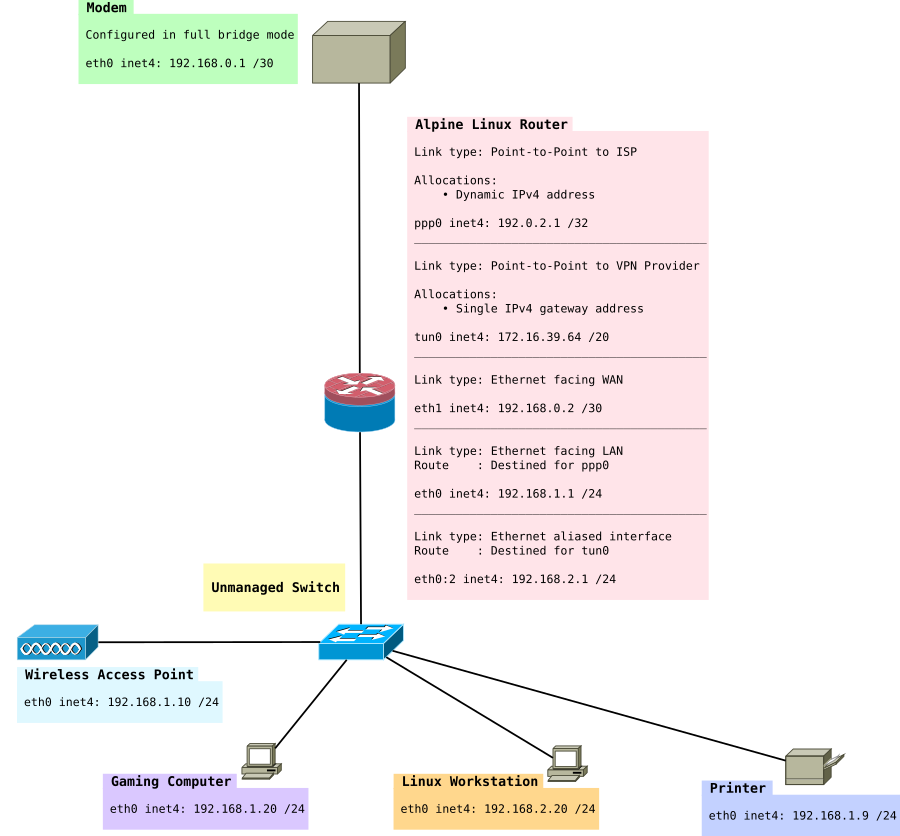
Install the necessary packages:
apk add openvpn iproute2 iputils
/etc/modules
You'll want to add the tun module
tun
/etc/iproute2/rt_tables
Add the two routing tables to the bottom of rt_tables. It should look something like this:
# # reserved values # 255 local 254 main 253 default 0 unspec # # local # #1 inr.ruhep 1 ISP 2 VPN
/etc/network/interfaces
Next up add the virtual interface: eth0:2, just under eth0 will do, remember to add an auto command to the top.
auto eth0 auto eth0:2 auto eth1 auto lo auto ppp0 # Route to ISP subnet iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255 # Route to VPN subnet iface eth0:2 inet static address 192.168.2.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.2.255 post-up /etc/network/fwmark_rules
/etc/sysctl.conf
If you want to use fwmark rules you need to change this setting. It causes the router to still do source validation.
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 2
fwmark won't work if you have this set to 1.
/etc/network/fwmark_rules
In this file we want to put the fwmark rules and set the correct priorities.
#!/bin/sh # Normal packets to go direct out WAN /sbin/ip rule add fwmark 1 table ISP prio 100 # Put packets destined into VPN when VPN is up /sbin/ip rule add fwmark 2 table VPN prio 200 # Prevent packets from being routed out when VPN is down. # This prevents packets from falling back to the main table # that has a priority of 32766 /sbin/ip rule add prohibit fwmark 2 prio 300
/etc/ppp/ip-up
Next up we want to create the routes that should be run when PPP comes online. There are special hooks we can use in ip-up and ip-down to refer to the IP address, ppp man file - Scripts You can also read about them in your man file if you have ppp-doc installed.
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script is run by pppd when there's a successful ppp connection.
#
# Flush out any old rules that might be there
/sbin/ip route flush table ISP
# Add route to table from subnets on LAN
/sbin/ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 table ISP
/sbin/ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 dev eth0 table ISP
# Add route from IP given by ISP to the table
/sbin/ip rule add from ${IPREMOTE} table ISP prio 100
# Add a default route
/sbin/ip route add table ISP default via ${IPREMOTE} dev ${IFNAME}
/etc/ppp/ip-down
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script is run by pppd after the connection has ended.
#
# Delete the rules when we take the interface down
/sbin/ip rule del from ${IPREMOTE} table ISP prio 100
/etc/openvpn/route-up-fwmark.sh
OpenVPN needs similar routing scripts and it also has it's own special hooks that allow you to specify particular values. A full list is here OpenVPN man file - Environmental Variables
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script is run by OpenVPN when there's a successful VPN connection.
#
# Flush out any old rules that might be there
/sbin/ip route flush table VPN
# Add route to table from 192.168.2.0/24 subnet on LAN
/sbin/ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 dev eth0 table VPN
# Add route from VPN interface IP to the VPN table
/sbin/ip rule add from ${ifconfig_local} table VPN prio 200
# Add a default route
/sbin/ip route add default via ${ifconfig_local} dev ${dev} table VPN
/etc/openvpn/route-pre-down-fwmark.sh
#!/bin/sh
#
# This script is run by OpenVPN after the connection has ended
#
# Delete the rules when we take the interface down
/sbin/ip rule del from ${ifconfig_local} table VPN prio 200
What I did find was when starting and stopping the OpenVPN service if you used:
service openvpn stop
The rules in route-pre-down-fwmark.sh were not executed.
However:
/etc/init.d/openvpn stop
seemed to work correctly.
Advanced IPtables rules that allow us to route into our two routing tables
This is an expansion of the previous set of rules. It sets up NAT masquerading for the 192.168.2.0 to go through the VPN using marked packets.
I used these guides to write complete this:
- Conning the Mark: Multiwan connections using IPTables, MARK, CONNMARK and iproute2
- Multiwan connections addendum
- Netfilter packet flow
######################################################################### # Advanced routing rule set # Uses 192.168.1.0 via ISP # 192.168.2.0 via VPN # # Packets to/from 192.168.1.0/24 are marked with 0x1 and routed to ISP # Packets to/from 192.168.2.0/24 are marked with 0x2 and routed to VPN # ######################################################################### # # NAT Table # This is where translation of packets happens and "forwarding" of ports # to specific hosts. # *nat # Set default policies for table :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Port forwarding for Bittorrent -A PREROUTING -i tun0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.20 -A PREROUTING -i tun0 -p udp -m udp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.20 # Allows routing to our modem subnet so we can access the web interface -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j MASQUERADE # Allows hosts of the network to use the VPN tunnel -A POSTROUTING -o tun0 -j MASQUERADE # Allows hosts of the network to use the PPP tunnel -A POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT # # Filter Table # This is where we decide to ACCEPT, DROP or REJECT things # *filter :INPUT DROP [0:0] :FORWARD DROP [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for forwarding packets :FWD_ETH0 - [0:0] :FWD_ETH1 - [0:0] :FWD_PPP0 - [0:0] :FWD_TUN0 - [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for input packets (for host itself) :IN_ETH0 - [0:0] :IN_ETH1 - [0:0] :IN_PPP0 - [0:0] :IN_TUN0 - [0:0] # Create a log drop chain :LOG_DROP - [0:0] # Create a reject chain :LOG_REJECT - [0:0] # Pass input packet to corresponding rule chain -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -j IN_ETH0 -A INPUT -i eth1 -j IN_ETH1 -A INPUT -i ppp0 -j IN_PPP0 -A INPUT -i tun0 -j IN_TUN0 # Track forwarded packets -A FORWARD -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Pass forwarded packet to corresponding rule chain -A FORWARD -i eth0 -j FWD_ETH0 -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j FWD_ETH1 -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -j FWD_PPP0 -A FORWARD -i tun0 -j FWD_TUN0 # Forward traffic to ISP -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Forward traffic to VPN -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Allow excepted server to be FORWARD to ppp0 #-A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT # Forward SSH packets from network to modem -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward HTTP packets from network to modem -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward Bittorrent Port to workstation -A FWD_TUN0 -d 192.168.2.20/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 6881:6889 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_TUN0 -d 192.168.2.20/32 -p udp -m udp --dport 6881:6889 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # SSH to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # DNS to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT # FreeRadius Client (eg a UniFi AP) -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Ubiquiti UAP Device Discovery Broadcast -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 10001 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # NTP to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept traffic to router on both subnets -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Allow excepted server to be INPUT to eth0 from LAN #-A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT # SSH To Modem from Router -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # HTTP To Modem from Router -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept incoming tracked PPP0 connection -A IN_PPP0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Log dropped packets coming in on PPP0 -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG --log-prefix "DROP:INPUT " --log-level 6 -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG_DROP # Accept incoming tracked TUN0 connection -A IN_TUN0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Log dropped packets coming in on TUN0 -A IN_TUN0 -j LOG --log-prefix "DROP:INPUT " --log-level 6 -A IN_TUN0 -j LOG_DROP COMMIT # # Mangle Table # This is the place where our markings happen, whether they be 0x1 or 0x2 # *mangle # Set default policies for table :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Restore CONNMARK to the MARK (If one doesn't exist then no mark is set) -A PREROUTING -j CONNMARK --restore-mark --nfmask 0xffffffff --ctmask 0xffffffff # If packet MARK is 2, then it means there is already a connection mark and the # original packet came in on VPN -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m mark --mark 0x2 -j ACCEPT # Check exception (this is a server which when accessed on a 192.168.2.0/24 address will go out the ISP table) are 0x1 #-A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -m mark --mark 0x1 -j ACCEPT # Mark packets coming from 192.168.2.0/24 are 0x2 -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x2/0xffffffff # If packet MARK is 1, then it means there is already a connection mark and the # original packet came in on ISP -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m mark --mark 0x1 -j ACCEPT # Mark packets 192.168.1.0/24 are 0x1 -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x1/0xffffffff # Mark exception (this is a server which when accessed on a 192.168.2.0/24 address will go out the ISP table) as 0x1 #-A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x1/0xffffffff # Set mark to 0 - This is for the modem. Otherwise it will mark with 0x1 or 0x2 -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.1/32 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x0/0xffffffff # Save MARK to CONNMARK (remember iproute can't see CONNMARKs) -A PREROUTING -j CONNMARK --save-mark --nfmask 0xffffffff --ctmask 0xffffffff COMMIT
You may want to delete certain rules here that do not apply to you, eg the FreeRadius rules. That is covered later in this article.
OpenVPN Routing
Usually when you connect with OpenVPN the remote VPN server will push routes down to your system. We don't want this as we still want to be able to access the internet without the VPN. We have also created our own routes that we want to use earlier in this guide.
You'll need to add this to the bottom of your OpenVPN configuration file:
# Prevents default gateway from being set on the default routing table route-noexec # Allows route-up script to be executed script-security 2 # Calls custom shell script after connection to add necessary routes route-up /etc/openvpn/route-up-fwmark.sh route-pre-down /etc/openvpn/route-pre-down-fwmark.sh
My VPNs are arranged like this in /etc/openvpn:
OpenVPN configuration file for that server:
countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn.conf
OpenVPN certs for that server:
countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn/countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn.crt countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn/countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn.key countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn/myKey.crt countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn/myKey.key
So I use this helpful script to automate the process of changing between servers:
#!/bin/sh
vpn_server_filename=$1
rm /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
ln -s $vpn_server_filename /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
chown -R openvpn:openvpn /etc/openvpn
chmod -R a=-rwx,u=+rX /etc/openvpn
chmod u=x /etc/openvpn/*.sh*
if grep -Fxq "#CustomStuffHere" openvpn.conf
then
echo "Not adding custom routes, this server has been used previously"
else
echo "Adding custom route rules"
echo -e "#CustomStuffHere\
\n# Prevents default gateway from being set on the default routing table\
\nroute-noexec\
\n# Allows route-up script to be executed\
\nscript-security 2 \
\n# Calls custom shell script after connection to add necessary routes\
\nroute-up /etc/openvpn/route-up-fwmark.sh\
\nroute-pre-down /etc/openvpn/route-pre-down-fwmark.sh\
\n# Logging of OpenVPN to file\
\n#log /etc/openvpn/openvpn.log"\
>> /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
fi
echo "Remember to set BitTorrent port forward in vcp.ovpn.to control panel"
That way I can simply change between servers by running:
changevpn.sh countrycode.serverNumber.openvpn
and then restart openvpn. I am also reminded to put the port forward through on the VPN control panel so my BitTorrent client is connectable:
service openvpn restart
Finally add openvpn to the default run level
rc-update add openvpn default
Creating a LAN only Subnet
In this section, we'll be creating a LAN only subnet. This subnet will be 192.168.3.0/24. The idea of this subnet is nodes in it cannot have their packets forwarded to the Internet, however they can be accessed via the other LAN subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24. This approach doesn't use VLANs although that would be recommended if you had a managed switch. The idea of this subnet is for things like WiFi access points, IP Phones which contact a local Asterisk server and of course printers.
At the end of this section we will have something like:
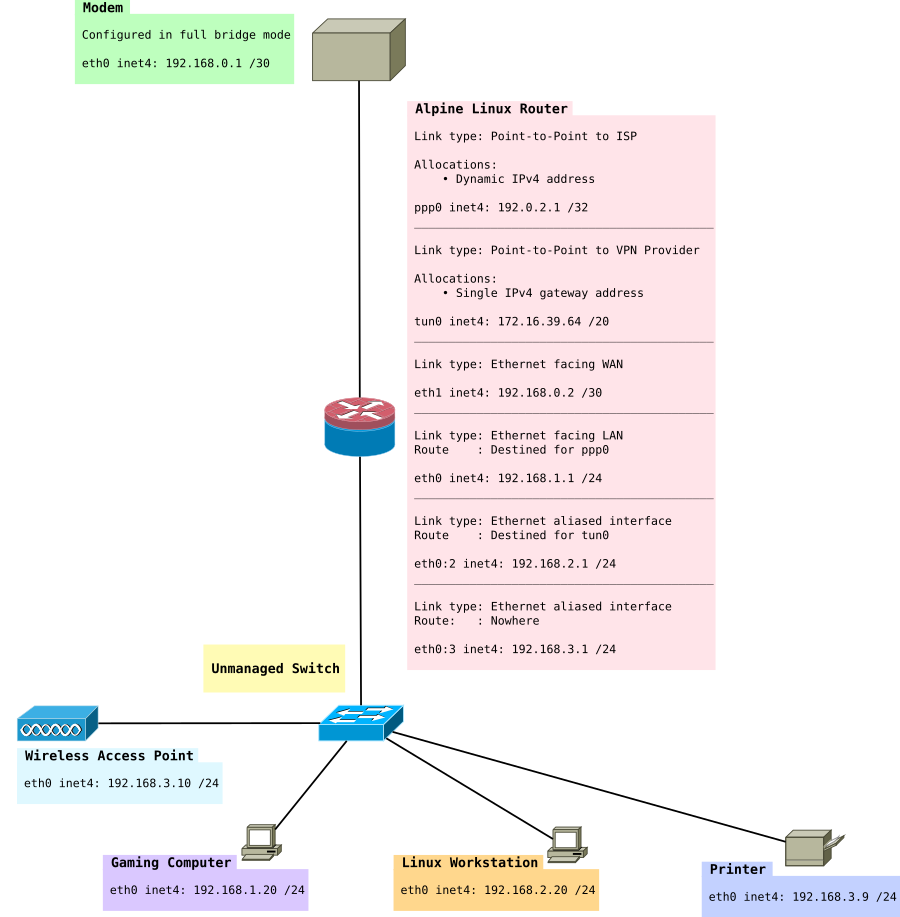
/etc/iproute2/rt_tables
First up we'll add a third routing table:
3 LAN
/etc/network/interfaces
Add a an extra interface.
auto eth0 auto eth0:2 auto eth0:3 auto eth1 auto lo auto ppp0 # LAN Only iface eth0:3 inet static address 192.168.3.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.3.255 post-up /etc/network/route_LAN
/etc/network/route_LAN
This file will have our route added to it
#!/bin/sh # Add routes from ISP to LAN /sbin/ip route add 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth0 table LAN # Add route from VPN to LAN /sbin/ip route add 192.168.2.0/24 dev eth0 table LAN # Add route from LAN to it's own table /sbin/ip route add 192.168.3.0/24 dev eth0 table LAN
/etc/ppp/ip-up
Append a route from the LAN subnet to the ISP table
# Add route to LAN subnet /sbin/ip route add 192.168.3.0/24 dev eth0 table ISP
/etc/openvpn/route-up-fwmark.sh
Append a route from the LAN subnet to the VPN table
# Add route to LAN only subnet /sbin/ip route add 192.168.3.0/24 dev eth0 table VPN
/etc/ntpd.conf
Add a listen address for ntp (OpenNTPD).
You should now have:
# Addresses to listen on (ntpd does not listen by default) listen on 192.168.1.1 listen on 192.168.2.1 listen on 192.168.3.1
Devices needing the correct time will need to use this NTP server because they will not be able to get it from the Internet.
Blocking bogons
Our LAN now has 4 subnets in total that are possible:
- 192.168.0.0/30 (connection between modem and router)
- 192.168.1.0/24 (ISP table, directly routed out WAN)
- 192.168.2.0/24 (VPN table, routed out VPN)
- 192.168.3.0/24 (Null routed subnet for LAN only hosts)
- 172.16.32.0/20 (VPN provider's network, so we can access things on the VPN's network).
Everything else should be rejected. No packets should ever be forwarded on 192.168.5.2 or 10.0.0.5 for example.
Installing ipset
Install ipset:
apk add ipset
Add it to start up:
rc-update add ipset default
Now we need to load the lists of addresses into ipset Securing Your Server using IPset and Dynamic Blocklists mentions a script which was particularly useful. This script could be run on a cron job if you wanted to regularly update it and for the full bogon list you should as they change when that address space has been allocated.
For the purpose of this we will be using just the bogon-bn-nonagg.txt list.
0.0.0.0/8 10.0.0.0/8 100.64.0.0/10 127.0.0.0/8 169.254.0.0/16 172.16.0.0/12 192.0.0.0/24 192.0.2.0/24 192.168.0.0/16 198.18.0.0/15 198.51.100.0/24 203.0.113.0/24 224.0.0.0/4 240.0.0.0/4
This is unlikely to change as it's the IPV4 Reserved IP addresses space. The script:
#! /bin/bash
# /usr/local/sbin/fullbogons-ipv4
# BoneKracker
# Rev. 11 October 2012
# Tested with ipset 6.13
# Purpose: Periodically update an ipset used in a running firewall to block
# bogons. Bogons are addresses that nobody should be using on the public
# Internet because they are either private, not to be assigned, or have
# not yet been assigned.
#
# Notes: Call this from crontab. Feed updated every 4 hours.
# target="http://www.team-cymru.org/Services/Bogons/fullbogons-ipv4.txt"
# Use alternative URL from pfSense, due to 404 error with URL above
target="https://files.pfsense.org/lists/bogon-bn-nonagg.txt"
ipset_params="hash:net"
filename=$(basename ${target})
firewall_ipset=${filename%.*} # ipset will be filename minus ext
data_dir="/var/tmp/${firewall_ipset}" # data directory will be same
data_file="${data_dir}/${filename}"
# if data directory does not exist, create it
mkdir -pm 0750 ${data_dir}
# function to get modification time of the file in log-friendly format
get_timestamp() {
date -r $1 +%m/%d' '%R
}
# file modification time on server is preserved during wget download
[ -w ${data_file} ] && old_timestamp=$(get_timestamp ${data_file})
# fetch file only if newer than the version we already have
wget -qNP ${data_dir} ${target}
if [ "$?" -ne "0" ]; then
logger -p cron.err "IPSet: ${firewall_ipset} wget failed."
exit 1
fi
timestamp=$(get_timestamp ${data_file})
# compare timestamps because wget returns success even if no newer file
if [ "${timestamp}" != "${old_timestamp}" ]; then
temp_ipset="${firewall_ipset}_temp"
ipset create ${temp_ipset} ${ipset_params}
#sed -i '/^#/d' ${data_file} # strip comments
sed -ri '/^[#< \t]|^$/d' ${data_file} # occasionally the file has been xhtml
while read network; do
ipset add ${temp_ipset} ${network}
done < ${data_file}
# if ipset does not exist, create it
ipset create -exist ${firewall_ipset} ${ipset_params}
# swap the temp ipset for the live one
ipset swap ${temp_ipset} ${firewall_ipset}
ipset destroy ${temp_ipset}
# log the file modification time for use in minimizing lag in cron schedule
logger -p cron.notice "IPSet: ${firewall_ipset} updated (as of: ${timestamp})."
fi
Now you should see the list loaded into memory when you do:
ipset list
We want to save it so our router can refer to it next time it starts up so for that:
/etc/init.d/ipset save
Adding our allowed networks
IPv4
ipset create allowed-nets-ipv4 hash:net,iface family inet
Then you can add each of your allowed networks:
ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 192.168.0.0/30,eth1 ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 192.168.1.0/24,eth0 ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 192.168.2.0/24,eth0 ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 192.168.3.0/24,eth0 ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 127.0.0.0/8,lo ipset add allowed-nets-ipv4 172.16.32.0/20,tun0
IPv6
For IPv6 if you've got any Unique local address ranges you may choose to add them:
ipset create allowed-nets-ipv6 hash:net,iface family inet6
ipset add allowed-nets-ipv6 fde4:8dba:82e1::/48,tun0 ipset add allowed-nets-ipv6 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::/64,eth0
Finally save the sets with this command so they can be loaded next boot:
/etc/init.d/ipset save
Restricting our LAN subnet with iptables, and blocking the bogons
Finally we can apply our iptables rules, to filter both 192.168.3.0/24 and make sure that subnets like 192.168.5.0/24 are not forwarded or accessible by our router. You will need to review these rules, and remove the ones that do not apply to you.
Don't forget to change your RADIUS rules if you moved your WiFi APs into the 192.168.3.0/24 subnet. You'll also need to edit /etc/raddb/clients.conf
I used a new table here called "raw". This table is more primitive than the filter table. It cannot have FORWARD rules or INPUT rules. Therefore you will still need a FORWARD rule in your filter table to block bogons originating from your LAN.
The only kind of rules we may use here are PREROUTING and OUTPUT. The OUTPUT rules will only filter traffic originating from our router's local processes, such as if we ran the ping command to a bogon range on the router's command prompt.
Traffic passes over the raw table, before connecting marking as indicated by this packet flow map: Netfilter packet flow graph this means we don't have to strip the mark off the bogon range in the mangle table anymore.
######################################################################### # Advanced routing rule set # Uses 192.168.1.0 via ISP # 192.168.2.0 via VPN # 192.168.3.0 via LAN # # Packets to/from 192.168.1.0/24 are marked with 0x1 and routed to ISP # Packets to/from 192.168.2.0/24 are marked with 0x2 and routed to VPN # Packets to/from 192.168.3.0/24 are routed to LAN and not forwarded onto # the internet # ######################################################################### # # Raw Table # This table is the place where we drop all illegal packets from networks that # do not exist # *raw :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] # Create a log drop chain :LOG_DROP_BOGON - [0:0] # Create an output chain :OUT_PPP0 - [0:0] :OUT_TUN0 - [0:0] # Allows traffic from VPN tunnel -A PREROUTING -s 172.16.32.0/20 -i tun0 -j ACCEPT # Allows traffic to VPN tunnel -A PREROUTING -d 172.16.32.0/20 -j ACCEPT # Block specified bogons coming in from ISP and VPN # (unlikely to happen as they filter them on their router) -A PREROUTING -i ppp0 -m set --match-set bogon-bn-nonagg src -j LOG_DROP_BOGON -A PREROUTING -i tun0 -m set --match-set bogon-bn-nonagg src -j LOG_DROP_BOGON # Allows my excepted ranges. -A PREROUTING -m set --match-set allowed-nets-ipv4 src,src -j ACCEPT # Pass output interface to corresponding chain -A OUTPUT -o ppp0 -j OUT_PPP0 -A OUTPUT -o tun0 -j OUT_TUN0 # Log drop chain -A LOG_DROP_BOGON -j LOG --log-prefix "Dropped Bogon (ipv4) : " --log-level 6 -A LOG_DROP_BOGON -j DROP # Block packets originating from the router destined to bogon ranges -A OUT_PPP0 -m set --match-set bogon-bn-nonagg dst -j LOG_DROP_BOGON # Blocks packets originating from the router destined to bogon ranges -A OUT_TUN0 -d 172.16.32.0/20 -j ACCEPT -A OUT_TUN0 -m set --match-set bogon-bn-nonagg dst -j LOG_DROP_BOGON COMMIT # # NAT Table # This is where translation of packets happens and "forwarding" of ports # to specific hosts. # *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Port forwarding for Bittorrent -A PREROUTING -i tun0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.20 -A PREROUTING -i tun0 -p udp -m udp --dport 6881:6889 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.2.20 # Allows routing to our modem subnet so we can access the web interface -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -o eth1 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j MASQUERADE # Allows hosts of the network to use the VPN tunnel -A POSTROUTING -o tun0 -j MASQUERADE # Allows hosts of the network to use the PPP tunnel -A POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT # # Filter Table # This is where we decide to ACCEPT, DROP or REJECT things # *filter :INPUT DROP [0:0] :FORWARD DROP [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for forwarding packets :FWD_ETH0 - [0:0] :FWD_ETH1 - [0:0] :FWD_PPP0 - [0:0] :FWD_TUN0 - [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for input packets (for host itself) :IN_ETH0 - [0:0] :IN_ETH1 - [0:0] :IN_PPP0 - [0:0] :IN_TUN0 - [0:0] # Create a drop chain :LOG_DROP - [0:0] # Create a log drop chain :LOG_DROP_BOGON - [0:0] # Create a reject chain :LOG_REJECT_LANONLY - [0:0] # Create an output chain :OUT_PPP0 - [0:0] :OUT_TUN0 - [0:0] # Pass input packet to corresponding rule chain -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -j IN_ETH0 -A INPUT -i eth1 -j IN_ETH1 -A INPUT -i ppp0 -j IN_PPP0 -A INPUT -i tun0 -j IN_TUN0 # Track forwarded packets -A FORWARD -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Pass forwarded packet to corresponding rule chain -A FORWARD -i eth0 -j FWD_ETH0 -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j FWD_ETH1 -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -j FWD_PPP0 -A FORWARD -i tun0 -j FWD_TUN0 # Pass output interface to corresponding chain -A OUTPUT -o ppp0 -j OUT_PPP0 -A OUTPUT -o tun0 -j OUT_TUN0 # Forward traffic to Modem -A FWD_ETH0 -d 192.168.0.1/32 -j ACCEPT # Allow routing to remote address on VPN -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 172.16.32.1/32 -o tun0 -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d 172.16.32.1/32 -o tun0 -j ACCEPT # Allow forwarding from LAN hosts to LAN ONLY subnet -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -d 192.168.3.0/24 -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d 192.168.3.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Allow LAN ONLY subnet to contact other LAN hosts -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.0/24 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.0/24 -d 192.168.2.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Refuse to forward bogons to the internet! -A FWD_ETH0 -m set --match-set bogon-bn-nonagg dst -j LOG_DROP_BOGON # Forward traffic to ISP -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Forward traffic to VPN -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -j ACCEPT # Prevent 192.168.3.0/24 from accessing internet -A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.0/24 -j LOG_REJECT_LANONLY # Allow excepted server to be FORWARD to ppp0 #-A FWD_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT # Forward SSH packets from network to modem -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward HTTP packets from network to mode -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Forward Bittorrent Port to workstation -A FWD_TUN0 -d 192.168.2.20/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 6881:6889 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A FWD_TUN0 -d 192.168.2.20/32 -p udp -m udp --dport 6881:6889 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # SSH to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # DNS to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT # FreeRadius Client (eg a UniFi AP) -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.10/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.10/32 -p udp -m udp --dport 1812 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Ubiquiti UAP Device Discovery Broadcast -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.10/32 -p udp -m udp --dport 10001 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # NTP to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.3.0/24 -p udp -m udp --dport 123 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept traffic to router on both subnets -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Allow excepted server to be INPUT to eth0 from LAN #-A IN_ETH0 -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -o ppp0 -j ACCEPT # SSH To Modem from Router -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # HTTP To Modem from Router -A IN_ETH1 -s 192.168.0.1/32 -d 192.168.0.0/30 -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Accept incoming tracked PPP0 connection -A IN_PPP0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Log dropped packets coming in on PPP0 -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG --log-prefix "DROP:INPUT (ipv4) " --log-level 6 -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG_DROP # Accept incoming tracked TUN0 connection -A IN_TUN0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Log dropped packets coming in on TUN0 -A IN_TUN0 -j LOG --log-prefix "DROP:INPUT (ipv4) " --log-level 6 -A IN_TUN0 -j LOG_DROP # Log dropped bogons that never got forwarded -A LOG_DROP_BOGON -j LOG --log-prefix "Dropped Bogon forward (ipv4) " --log-level 6 -A LOG_DROP_BOGON -j DROP # Log rejected packets -A LOG_REJECT_LANONLY -j LOG --log-prefix "Rejected packet from LAN only range : " --log-level 6 -A LOG_REJECT_LANONLY -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable COMMIT # # Mangle Table # This is the place where our markings happen, whether they be 0x1 or 0x2 # *mangle # Set default policies for table :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] # Restore CONNMARK to the MARK (If one doesn't exist then no mark is set) -A PREROUTING -j CONNMARK --restore-mark --nfmask 0xffffffff --ctmask 0xffffffff # If packet MARK is 2, then it means there is already a connection mark and the # original packet came in on VPN -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m mark --mark 0x2 -j ACCEPT # Check exception (this is a server which when accessed on a 192.168.2.0/24 address will go out the ISP table) are 0x1 #-A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -m mark --mark 0x1 -j ACCEPT # Mark packets coming from 192.168.2.0/24 are 0x2 -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x2/0xffffffff # If packet MARK is 1, then it means there is already a connection mark and the # original packet came in on ISP -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m mark --mark 0x1 -j ACCEPT # Mark packets 192.168.1.0/24 are 0x1 -A PREROUTING -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x1/0xffffffff # Mark exception (this is a server which when accessed on a 192.168.2.0/24 address will go out the ISP table) as 0x1 #-A PREROUTING -s 192.168.2.0/24 -d <IP_OF_EXCEPTED_SERVER>/32 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x1/0xffffff # Strip mark if packet is destined for modem -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.1/32 -j MARK --set-xmark 0x0/0xffffffff # Save MARK to CONNMARK (remember iproute can't see CONNMARKs) -A PREROUTING -j CONNMARK --save-mark --nfmask 0xffffffff --ctmask 0xffffffff COMMIT
IPv6
IPv6 introduces a number of new complexities into our network. To begin with we're going to build a basic IPv6 network without the VPN tunnel ie 192.168.2.0/24 subnet or tun0 interface. If you've completed previous parts of this guide, you can leave that part as is.
If your VPN provider only offers you a single stack connection (no IPv6) then you've got nothing there to worry about.
In this section we will implement IPv6 dual stack. We do at this point only have dual stack, prefix delegation. If you know nothing about IPv6, then you should have a look at these helpful pages:
- Linux IPv6 HOWTO (en) - in particular the "basics" and "address types".
- IPv6
- IPv6 Address
- Prefix delegation we use this with dhcpcd when doing DHCPv6-PD to inform our ISP of our network devices.
- Neighbor Discovery Protocol we use this with radvd to distribute our routes.
- Internet Control Message Protocol version 6 ICMPv6 differs from ICMPv4 and is used for many critical parts of IPv6 infrastructure.
- IPv6-test.com Useful for diagnosing if IPv6 is working.
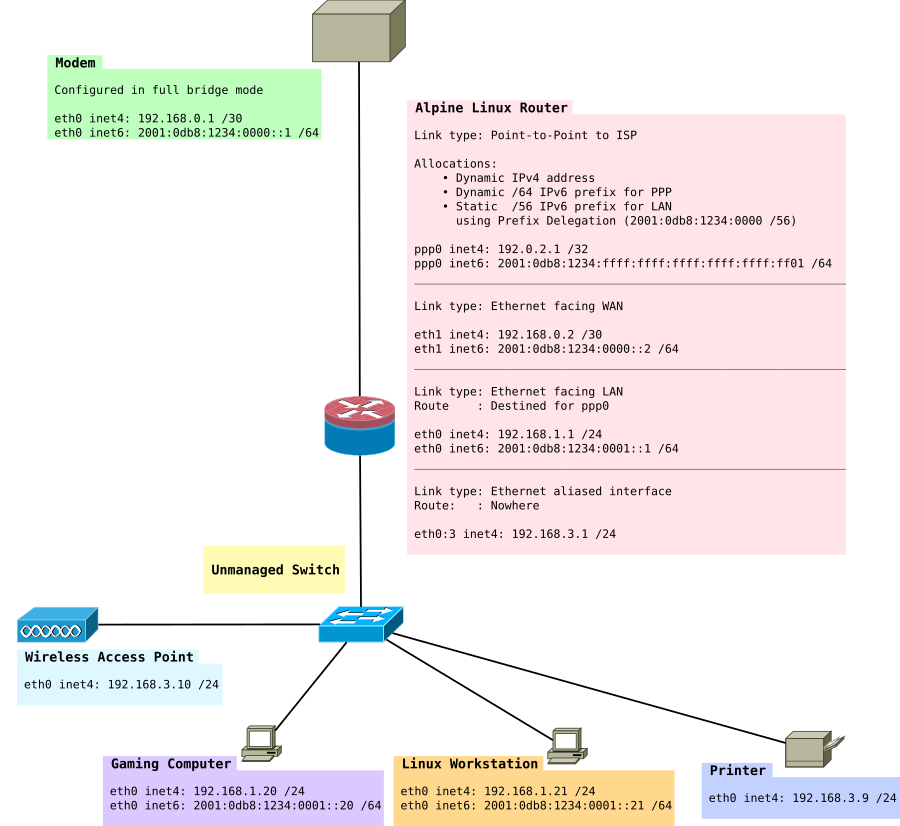
Enabling IPv6 support
Assuming you're using the Alpine Linux kernel, IPv6 support is available separately as a module.
modprobe ipv6
To add the module to our startup configuration.
echo "ipv6" >> /etc/modules
/etc/sysctl.conf
Modify the sysctl section to include IPv6 support:
######################################## ### IPv6 ### ######################################## # http://vk5tu.livejournal.com/37206.html # What's this special value "2"? Originally the value was "1", but this # disabled autoconfiguration on all interfaces. That is, you couldn't appear # to be a router on some interfaces and appear to be a host on other # interfaces. But that's exactly the mental model of a ADSL router. # Controls IP packet forwarding net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 2 net.ipv6.conf.default.forwarding = 2 # Enable source validation by reversed path # Protects from attackers that are using ip spoofing methods to do harm net.ipv6.conf.all.rp_filter = 1 net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra = 2 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_ra = 2 # Disable redirects, not a router net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
/etc/ppp/peers/yourISP
Add this to your ppp configuration. This tells PPP to get an ipv6 address. Note the comma is needed.
# Enable IPV6 +ipv6 ipv6cp-use-ipaddr ipv6 ,
Check system log
Restart ppp.
poff yourISP
pon yourISP
In /var/log/messages you should see something like
pppd[]: Plugin rp-pppoe.so loaded. pppd[]: RP-PPPoE plugin version 3.8p compiled against pppd 2.4.7 pppd[]: pppd 2.4.7 started by root, uid 0 pppd[]: PPP session is 49969 pppd[]: Connected to 00:53:00:ff:ff:f0 via interface eth1 pppd[]: Using interface ppp0 pppd[]: Connect: ppp0 <--> eth1 pppd[]: CHAP authentication succeeded pppd[]: CHAP authentication succeeded pppd[]: peer from calling number 00:53:00:FF:FF:F0 authorized pppd[]: local LL address fe80::0db8:ffff:ffff:fff1 pppd[]: remote LL address fe80::0db8:ffff:ffff:fff0 pppd[]: local IP address 192.0.2.1 pppd[]: remote IP address 192.0.2.0 pppd[]: primary DNS address 192.0.2.10 pppd[]: secondary DNS address 192.0.2.20
You should be able to now ping things such as
ping6 ipv6.google.com
from your router.
Prefix Delegation
The next step will be to configure DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation with your ISP. Install dhcpcd. While many guides do use the wide-dhcpv6-client it should be noted this is unmaintained and not included in Alpine Linux.
Don't use the ISC's dhclient either as this does not support Prefix Delegations on PPP links without a patch.
apk add dhcpcd
You can check out the manual for dhcpcd.conf. Installing dhcpcd-doc will allow you to read the man file. Eg:
apk add dhcpcd-doc
/etc/dhcpcd.conf
apk add dhcpcd
# Enable extra debugging
# debug
# Allow users of this group to interact with dhcpcd via the control
# socket.
#controlgroup wheel
# Inform the DHCP server of our hostname for DDNS.
hostname gateway
# Use the hardware address of the interface for the Client ID.
#clientid
# or
# Use the same DUID + IAID as set in DHCPv6 for DHCPv4 ClientID as
# per RFC4361. Some non-RFC compliant DHCP servers do not reply with
# this set. In this case, comment out duid and enable clientid above.
duid
# Persist interface configuration when dhcpcd exits.
persistent
# Rapid commit support.
# Safe to enable by default because it requires the equivalent option
# set on the server to actually work.
option rapid_commit
# A list of options to request from the DHCP server.
option domain_name_servers, domain_name, domain_search, host_name
option classless_static_routes
# Most distributions have NTP support.
option ntp_servers
# Respect the network MTU.
# Some interface drivers reset when changing the MTU so disabled by
# default.
#option interface_mtu
# A ServerID is required by RFC2131.
require dhcp_server_identifier
# Generate Stable Private IPv6 Addresses instead of hardware based
# ones
slaac private
# A hook script is provided to lookup the hostname if not set by the
# DHCP server, but it should not be run by default.
nohook lookup-hostname
# IPv6 Only
ipv6only
# Disable solicitations on all interfaces
noipv6rs
# Wait for IP before forking to background
waitip 6
# Don't install any default routes.
# PPP has already set a default route
nogateway
# Don't touch DNS
nohook resolv.conf
# Use the interface connected to WAN
interface ppp0
ipv6rs # enable routing solicitation get the default IPv6 route
iaid 1
ia_pd 1/::/64 eth0/1/64 # Assign a prefix delegated route to our LAN
Add dhcpcd to the default run level:
rc-update add dhcpcd default
Configure ip6tables with a basic ruleset
A basic rule set for ip6tables. It is commented so feel free to read it.
You'll need to modify your prefix in one of the rules.
######################################################################### # Basic iptables IPv6 routing rule set # # 2001:0db8:1234:0001 /64 hosts routed directly to ppp0 # ######################################################################### # # Filter Table # This is where we decide to ACCEPT, DROP or REJECT things # *filter :INPUT DROP [0:0] :FORWARD DROP [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for forwarding packets :FWD_ETH0 - [0:0] :FWD_ETH1 - [0:0] :FWD_PPP0 - [0:0] :FWD_TUN0 - [0:0] # Create rule chain per input interface for input packets (for host itself) :IN_ETH0 - [0:0] :IN_ETH1 - [0:0] :IN_PPP0 - [0:0] # Create a drop chain :LOG_DROP - [0:0] # Accept all from localhost -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT # Create rule chain per input interface for input packets (for host itself) -A INPUT -i eth0 -j IN_ETH0 -A INPUT -i eth1 -j IN_ETH1 -A INPUT -i ppp0 -j IN_PPP0 # Track forwarded packets -A FORWARD -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Pass forwarded packet to corresponding rule chain -A FORWARD -i eth0 -j FWD_ETH0 -A FORWARD -i eth1 -j FWD_ETH1 -A FORWARD -i ppp0 -j FWD_PPP0 # Rate limit ICMPv6 -A FORWARD -p ipv6-icmp -m icmp6 --icmpv6-type 128 -m limit --limit 30/min -j ACCEPT # Forward LAN subnet -A FWD_ETH0 -s 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64 -j ACCEPT # Accept all ICMPv6 from LAN -A IN_ETH0 -p ipv6-icmp -j ACCEPT # DNS to Router -A IN_ETH0 -s 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -j ACCEPT # LAN traffic out -A IN_ETH0 -s 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64 -m conntrack --ctstate NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Rate limit ICMPv6 coming in from outside -A IN_PPP0 -p ipv6-icmp -m icmp6 --icmpv6-type 128 -m limit --limit 30/min -j ACCEPT # Accept tracked connections from outside -A IN_PPP0 -m conntrack --ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Drop and log everything else -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG --log-prefix "DROP:INPUT (ipv6) " --log-level 6 -A IN_PPP0 -j LOG_DROP COMMIT *raw :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] COMMIT *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] COMMIT *mangle :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] COMMIT
Add ip6tables to the default run level:
rc-update add ip6tables default
Router Advertisements
apk add radvd
Once radvd is installed, you may configure it:
/etc/radvd.conf
Note this will cause an IPv6 address to be routed to your systems. Those systems will now leak via IPv6 to the Internet if you're on a subnet like 192.168.2.0/24 using an aliased connection.
To mitigate this we would use VLANs, which behave as separate network interfaces. For that you need to replaced the unmanaged switch with a managed one, and each interface, eg eth0:2 with eth0.2.
interface eth0 {
# We are sending advertisements (route)
AdvSendAdvert on;
# Suggested Maximum Transmission setting for using the
# Hurricane Electric Tunnel Broker.
# AdvLinkMTU 1480;
# We have native Dual Stack IPv6 so we can use the regular MTU
# http://blogs.cisco.com/enterprise/ipv6-mtu-gotchas-and-other-icmp-issues
AdvLinkMTU 1500;
prefix 2001:0db8:1234:b001::/64 {
AdvOnLink on;
AdvAutonomous on; # SLAAC based on EUI
AdvRouterAddr on;
};
RDNSS 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1 {
};
# DNSSL example.id.au {
# };
};
Add radvd to the default run level:
rc-update add radvd default
Enable Privacy extensions in /etc/sysctl.conf
When a client acquires an address through SLAAC its IPv6 address is derived from the advertised prefix and the MAC address of the network interface of the client. This may raise security concerns as the MAC address of the computer can be easily derived by the IPv6 address. In order to tackle this problem the IPv6 Privacy Extensions standard (RFC 4941) has been developed. With privacy extensions the kernel generates a temporary address that is mangled from the original autoconfigured address. Private addresses are preferred when connecting to a remote server so the original address is hidden. To enable Privacy Extensions reproduce the following steps:
# Enable IPv6 Privacy Extensions net.ipv6.conf.all.use_tempaddr = 2 net.ipv6.conf.default.use_tempaddr = 2 net.ipv6.conf.nic0.use_tempaddr = 2 ... net.ipv6.conf.nicN.use_tempaddr = 2
Using DHCPv6
You may decide you want more control over your network address assignment. For this you'll need to use DHCPv6. DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 need to run on separate instances of DHCPD.
Make a symlink for the init script:
ln -s /etc/init.d/dhcpd /etc/init.d/dhcpdv6
Include it in the router provision file:
lbu include /etc/init.d/dhcpdv6
Copy the DHCP Daemon configuration file:
cp /etc/conf.d/dhcpd /etc/conf.d/dhcpdv6
Enable it to run on IPv6. DHCPD can only run on one IP protocol at a time. By default it defaults to IPv4.
sed -i 's/# DHCPD_OPTS=""/DHCPD_OPTS="-6"/g' /etc/conf.d/dhcpdv6
Copy the DHCP configuration file:
cp /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf /etc/dhcp/dhcpdv6.conf
Chown the configurations
chown -R dhcp:dhcp /etc/dhcp
/etc/dhcp/dhcpdv6.conf
You will want to edit your MAC address in the host declarations. The client-id or DUID can be found in /etc/dhcpcd.duid when you've installed dhcpcd on your client.
You can also see it in /var/log/messages on your router when a client tries to authenticate on your network eg:
dhcpd: Advertise NA: address 2001:0db8:1234:0001::240 to client with duid <DEVICE DUID> iaid = <DEVICE IAID> valid for 43200 seconds
Currently Android does not have DHCPv6 support and Google seem unwilling to add it.
If you're using a version of dhcpcd below 6.9.3 you may need to set "ipv6ra_accept_nopublic" in your /etc/dhcpcd.conf.
authoritative;
ddns-update-style interim;
shared-network home {
subnet6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64 {
range6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::10 2001:0db8:1234:0001::240;
range6 2001:0db8:1234:0001:: temporary;
option dhcp6.name-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
option dhcp6.sntp-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
allow unknown-clients;
}
subnet6 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::/64 {
range6 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::10 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::240;
range6 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff:: temporary;
option dhcp6.name-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
option dhcp6.sntp-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
ignore unknown-clients;
}
}
host Gaming_Computer {
hardware ethernet 00:53:00:FF:FF:11;;
host-identifier option dhcp6.client-id <YOUR_DUID>;
fixed-address6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::20;
fixed-prefix6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64;
option dhcp6.name-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
option dhcp6.sntp-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
}
host Linux Workstation {
hardware ethernet 00:53:00:FF:FF:22;;
host-identifier option dhcp6.client-id <YOUR_DUID>;
fixed-address6 fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::21;
fixed-prefix6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::/64;
option dhcp6.name-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
option dhcp6.sntp-servers 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1;
}
Other Tips
Diagnosing firewall problems
netcat, netcat6
Netcat can be useful for testing if a port is open or closed or filtered.
apk add netcat-openbsd
After installing netcat we can use it like this:
Say we wanted to test for IPv6, UDP, Port 547 we would do this on the router:
nc -6 -u -l 547
and then this on the client to connect to it:
nc -u -v -6 2001:0db8:1234:0001::1 547
tcpdump
tcpdump can also be useful for dumping the contents of packets coming in on an interface:
apk add tcpdump
Then we can run it. This example captures all DNS traffic originating from 192.168.2.20.
tcpdump -i eth0 udp and src 192.168.2.20 and port 53
You can write the file out with the -w option, and view it in Wireshark locally on your computer. You can increase the verbosity with the -v option. Using -vv will be even more verbose. -vvv will show even more.
lbu cache
Configure lbu cache so that you don't need to download packages when you restart your router eg Local APK cache
This is particularly important as some of the images do not contain ppp-pppoe. This might mean you're unable to get an internet connection to download the other packages on boot.
lbu encryption /etc/lbu/lbu.conf
In /etc/lbu/lbu.conf you might want to enable encryption to protect your VPN keys.
# what cipher to use with -e option DEFAULT_CIPHER=aes-256-cbc # Uncomment the row below to encrypt config by default ENCRYPTION=$DEFAULT_CIPHER # Uncomment below to avoid <media> option to 'lbu commit' # Can also be set to 'floppy' LBU_MEDIA=mmcblk0p1 # Set the LBU_BACKUPDIR variable in case you prefer to save the apkovls # in a normal directory instead of mounting an external media. # LBU_BACKUPDIR=/root/config-backups # Uncomment below to let lbu make up to 3 backups # BACKUP_LIMIT=3
Remember to set a root password, by default Alpine Linux's root account is passwordless.
passwd root
Backup apkprov
It's a good idea to back up your apk provision file. You can pull it off your router to your local workstation with:
scp -r root@192.168.2.1:/media/mmcblk0p1/<YOUR HOST NAME>.apkovl.tar.gz.aes-256-cbc ./
And decrypt it with:
openssl enc -d -aes-256-cbc -in <YOUR HOST NAME>.apkovl.tar.gz.aes-256-cbc -out <YOUR HOST NAME>.apkovl.tar.gz
It can be encrypted with:
openssl aes-256-cbc -salt -in <YOUR HOST NAME>.apkovl.tar.gz -out <YOUR HOST NAME>.apkovl.tar.gz.aes-256-cbc
Harden SSH
Generate a SSH key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
You will want to put the contents of id_rsa.pub in /etc/ssh/authorized_keys
You can put multiple public keys on multiple lines if more than one person has access to the router.
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
A couple of good options to set in here can be:
ListenAddress 192.168.1.1 ListenAddress 192.168.2.1
While this isn't usually a good idea, a router doesn't need more than one user.
PermitRootLogin yes
The most important options:
RSAAuthentication yes PubkeyAuthentication yes AuthorizedKeysFile /etc/ssh/authorized_keys PasswordAuthentication no PermitEmptyPasswords no AllowTcpForwarding no X11Forwarding no
/etc/conf.d/sshd
You will want to add
rc_need="net"
This instructs OpenRC to make sure the network is up before starting ssh.
Finally add sshd to the default run level
rc-update add sshd default