LXC: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Create a guest == | == Create a guest == | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t alpine}} | {{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t alpine}} | ||
This will create a ''/var/lib/lxc/guest1'' directory with a ''config'' file and a ''rootfs'' directory. | This will create a ''/var/lib/lxc/guest1'' directory with a ''config'' file and a ''rootfs'' directory. | ||
=== Debian template === | === Debian template === | ||
| Line 50: | Line 45: | ||
Now you can run: | Now you can run: | ||
{{Cmd|SUITE=wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t debian}} | {{Cmd|SUITE{{=}}wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t debian}} | ||
== Starting/Stopping the guest == | == Starting/Stopping the guest == | ||
Revision as of 10:42, 2 October 2013
Linux Containers (LXC) provides containers similar BSD Jails, Linux VServer and Solaris Zones. It gives the impression of virtualization, but shares the kernel and resources with the "host".
Installation
Install the required packages:
apk add lxc bridge
Prepare network on host
Set up a bridge on the host. Example /etc/network/interfaces:
auto br0
iface br0 inet dhcp
bridge-ports eth0
Create a network configuration template for the guests, /etc/lxc/lxc.conf:
lxc.network.type = veth lxc.network.link = br0 lxc.network.flags = up
Create a guest
lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t alpine
This will create a /var/lib/lxc/guest1 directory with a config file and a rootfs directory.
Debian template
In order to create a debian template container you will need to install some packages:
apk add debootstrap rsync
Also you will need to turn off some grsecurity chroot options otherwise the debootstrap will fail:
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chroot echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mount echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mknod echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chmod
Please remember to turn them back on, or just simply reboot the system.
Now you can run:
SUITE=wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/lxc.conf -t debian
Starting/Stopping the guest
Create a symlink to the /etc/init.d/lxc script for your guest.
ln -s lxc /etc/init.d/lxc.guest1
You can start your guest with:
/etc/init.d/lxc.guest1 start
Stop it with:
/etc/init.d/lxc.guest1 stop
Make it autostart on boot up with:
rc-update add lxc.guest1
Connecting to the guest
By default sshd is not installed, so you will have to connect to a virtual console. This is done with:
lxc-console -n guest1
To disconnect from it, press Ctrl+a q
Deleting a guest
Make sure the guest is stopped and run:
lxc-destroy -n guest1
This will erase eerything, without asking any questions. It is equivalent to:
rm -r /var/lib/lxc/guest1
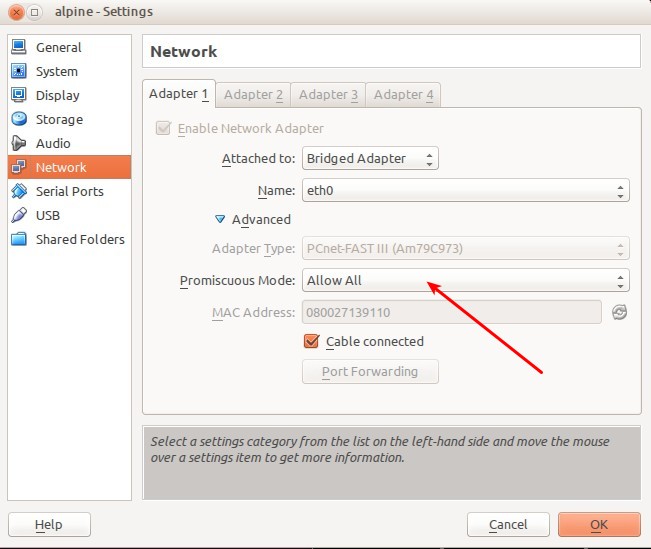
VirtualBox
In order for network to work on containers you need to set "Promiscuous Mode" to "Allow All" in VirtualBox settings for the network adapter.