LXC: Difference between revisions
m (update link to LXC homepage) |
Prabuanand (talk | contribs) m (moved category to the bottom of the page) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[https://linuxcontainers.org/ Linux Containers (LXC)] provides containers similar BSD Jails, Linux | [https://linuxcontainers.org/ Linux Containers (LXC)] provides containers similar to BSD Jails, Linux VServers and Solaris Zones. It gives the impression of virtualization, but shares the kernel and resources with the "host". You can use lxc directly or through [[LXD]]. | ||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
Install the required packages: | Install the required packages: | ||
{{Cmd|apk add lxc bridge}} | {{Cmd|apk add lxc bridge lxcfs lxc-download xz}} | ||
If you want to create containers other | If you want to create containers other than Alpine, you'll need lxc-templates: | ||
{{Cmd|apk add lxc-templates}} | {{Cmd|apk add lxc-templates}} | ||
== Upgrading from 2.x == | |||
Starting with Alpine 3.9, we ship LXC version 3.1. | |||
LXC 3.x has major changes which can and will break your current setup. | |||
LXC 3.x will NOT ship with legacy container templates. Check your current container configs to see if you have any includes pointing to files that don't exist (shipped by legacy templates). | |||
For example if you use Alpine containers created with the Alpine template, you'll need to install: | |||
apk add lxc-templates-legacy-alpine | |||
Also make sure you convert your LXC config files to the new 2.x format (this is now required). | |||
lxc-update-config -c /var/lib/lxc/container-name/config | |||
Make sure you have removed '''cgroup_enable''' from your cmdline as this will fail to mount cgroups and fail LXC service. | |||
== Prepare network on host == | == Prepare network on host == | ||
Install the {{Pkg|lxc-bridge}} package to create the <code>lxcbr0</code> bridge and configure the forwarding routes using iptables | |||
apk add lxc-bridge iptables | |||
Enable the dnsmasq [[OpenRC]] service at boot and start it | |||
rc-update add dnsmasq.lxcbr0 boot | |||
service dnsmasq.lxcbr0 start | |||
If you dont want to forward the routes, add <code>DISABLE_IPTABLES="yes"</code> to the /etc/conf.d/dnsmasq.lxcbr0 file | |||
=== Assign static IP for a container === | |||
Using the dnsmasq method you can leave the container interface asking for DHCP as it is. You will just need to set the DHCP server asnwers. | |||
By editing the file /etc/lxc/dnsmasq.conf and add the hostname (container name) and desired ip | |||
dhcp-host=guest1,10.0.3.4 | |||
dhcp-host=guest2,10.0.3.5 | |||
Restart the service | |||
service dnsmasq.lxcbr0 restart | |||
== Create a guest == | == Create a guest == | ||
=== Picking from the list === | |||
{{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t download}} | |||
And just pick from the list. lxc-download and xz can be uninstalled after you are done. | |||
=== Alpine Template === | === Alpine Template === | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/ | {{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t alpine}} | ||
This will create a ''/var/lib/lxc/guest1'' directory with a ''config'' file and a ''rootfs'' directory. | This will create a ''/var/lib/lxc/guest1'' directory with a ''config'' file and a ''rootfs'' directory. | ||
Note | Note: by default, the alpine template '''does not have networking service on''', you will need to add it using lxc-console | ||
If running on | If running on x64 compatible hardware, it is possible to create a 32bit guest: | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/ | {{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t alpine -- --arch x86}} | ||
=== Debian template === | === Debian template === | ||
In order to create a debian template container you | In order to create a debian template container you'll need to install some packages: | ||
{{Cmd|apk add debootstrap rsync}} | {{Cmd|apk add debootstrap rsync}} | ||
You'll need to turn off some grsecurity chroot options otherwise the debootstrap will fail: | |||
{{Cmd|echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps | {{Cmd|echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
}} | }} | ||
Remember to turn them back on, or simply reboot. | |||
Now you can run: | Now you can run: | ||
{{Cmd|SUITE{{=}}wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/ | {{Cmd|SUITE{{=}}wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t debian}} | ||
==== Setting a static IP ==== | |||
Since Debian Bullseye 11.3 you can't assign a static IP address using the lxc config file of the container [https://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=1009351 because of a systemd change]. | |||
To make it work with a configuration like the following | |||
# grep net /var/lib/lxc/bullseye/config | |||
lxc.net.0.type = veth | |||
lxc.net.0.flags = up | |||
lxc.net.0.link = virbr1 | |||
lxc.net.0.ipv4.address = 192.168.1.111/24 | |||
lxc.net.0.ipv4.gateway = 192.168.1.1 | |||
You have to attach to the container and run | |||
{{Cmd|lxc-attach -n bullseye | |||
systemctl stop systemd-networkd | |||
systemctl disable systemd-networkd | |||
reboot | |||
}} | |||
After the reboot the IP address should be set correctly. This can be confirmed using the lxc-ls command | |||
{{Cmd|# lxc-ls -f | |||
NAME STATE AUTOSTART GROUPS IPV4 IPV6 UNPRIVILEGED | |||
bullseye RUNNING 1 - 192.168.1.111 - false | |||
}} | |||
=== Ubuntu template === | === Ubuntu template === | ||
In order to create an ubuntu template container you | {{Obsolete|Alpine has not contained grsec for a long time}} | ||
In order to create an ubuntu template container, you'll need to turn off some grsecurity chroot options: | |||
{{Cmd|echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps | {{Cmd|echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps | ||
| Line 101: | Line 132: | ||
}} | }} | ||
Remember to turn them back on, or simply reboot. | |||
Now you can run (replace %MIRROR% with the actual hostname, for example: http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/) | Now you can run (replace %MIRROR% with the actual hostname, for example: http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/) | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-create -n guest2 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t ubuntu -- -r xenial -a amd64 -u user --password secretpassword --mirror $MIRROR }} | |||
{{Warning|Be sure to set systemd_container to yes in /etc/conf.d/lxc.CONTAINER. Otherwise, most functionality will be broken}} | |||
=== Unprivileged LXC images (Alpine / Debian / Ubuntu / Centos etc..) === | |||
To enable unprivileged containers, one must create a uidgid map: | |||
echo root:1000000:65536 | tee -a /etc/subuid | |||
echo root:1000000:65536 | tee -a /etc/subgid | |||
This creates a uid and gid map for the root user starting at 1000000 with a size of 65536. | |||
To configure containers to use this mapping, add the following lines to the configuration: | |||
lxc.idmap = u 0 1000000 65536 | |||
lxc.idmap = g 0 1000000 65536 | |||
This can be in the global or container-specific configuration. | |||
To create an unprivileged lxc container, you need to use the download template. The download template must be installed: | |||
{{Cmd|apk add gnupg xz | {{Cmd|apk add gnupg xz lxc-download | ||
lxc-create -n container-name -t download}} | lxc-create -n container-name -t download}} | ||
choose the Distribution | Release | Architecture. | |||
To be able to | To be able to log in to a Debian container, you currently need to: | ||
{{Cmd|rm /lib/systemd/system/container-getty\@.service}} | {{Cmd|rm /lib/systemd/system/container-getty\@.service}} | ||
You can also [ | You can also [https://without-systemd.org/wiki/index_php/How_to_remove_systemd_from_a_Debian_jessie/sid_installation/ remove Systemd from the container]. | ||
== Starting/Stopping the guest == | == Starting/Stopping the guest == | ||
First, you should enable the cgroup script: | |||
{{Cmd|rc-update add cgroups}} | |||
If you don't want to reboot, you can start the service by running | |||
{{Cmd|rc-service cgroups start}} | |||
Create a symlink to the ''/etc/init.d/lxc'' script for your guest. | Create a symlink to the ''/etc/init.d/lxc'' script for your guest. | ||
{{Cmd|ln -s lxc /etc/init.d/lxc.guest1}} | {{Cmd|ln -s lxc /etc/init.d/lxc.guest1}} | ||
You can start your guest with: | You can start your guest with: | ||
{{Cmd| | {{Cmd|rc-service lxc.guest1 start}} | ||
Stop it with: | Stop it with: | ||
{{Cmd| | {{Cmd|rc-service lxc.guest1 stop}} | ||
Make it autostart | Make it autostart at boot-up with: | ||
{{Cmd| rc-update add lxc.guest1}} | {{Cmd| rc-update add lxc.guest1}} | ||
You can | You can add to the container config: <code>lxc.start.auto = 1</code> | ||
{{Cmd|rc-update add lxc}} | |||
to autostart containers | to autostart containers with the lxc service only. | ||
== Connecting to the guest == | == Connecting to the guest == | ||
By default sshd is not installed | By default, sshd is not installed. You'll have to attach to the container or connect to the virtual console. This is done with: | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-attach -n guest1}} | {{Cmd|lxc-attach -n guest1}} | ||
Type exit to detach from the container again (please check the grsec notes above) | |||
== Connect to virtual console == | |||
{{Cmd|lxc-console -n guest1}} | {{Cmd|lxc-console -n guest1}} | ||
To disconnect | To disconnect, press {{key|Ctrl}}+{{key|a}} {{key|q}} | ||
== Deleting a guest == | == Deleting a guest == | ||
Make sure the guest is stopped | Make sure the guest is stopped, then run: | ||
{{Cmd|lxc-destroy -n guest1}} | {{Cmd|lxc-destroy -n guest1}} | ||
This will erase everything, without asking any questions. It is equivalent to: {{Cmd|rm -r /var/lib/lxc/guest1}} | This will erase everything, without asking any questions. It is equivalent to: {{Cmd|rm -r /var/lib/lxc/guest1}} | ||
| Line 163: | Line 218: | ||
The problem with bridging is that the interface you bridge gets replaced with your new bridge interface. | The problem with bridging is that the interface you bridge gets replaced with your new bridge interface. | ||
Let's say you have interface eth0 that you want to bridge. Your eth0 interface gets replaced with the br0 interface that you create. It also means that the interface you use needs to be placed into promiscuous mode to catch all the traffic that could be destined to the other side of the bridge, which may not be what you want. | |||
The solution is to create a dummy network interface, bridge that, and set up NAT so that traffic out of your bridge interface gets pushed through the interface of your choice. | The solution is to create a dummy network interface, bridge that, and set up NAT so that traffic out of your bridge interface gets pushed through the interface of your choice. | ||
Let's create that dummy interface (thanks to ncopa for talking me out of macvlan and pointing out the dummy interface kernel module) | |||
{{Cmd|modprobe dummy}} | {{Cmd|modprobe dummy}} | ||
This will create a dummy interface called dummy0 on your host. | This will create a dummy interface called dummy0 on your host. To create this interface on every boot, append "dummy" to /etc/modules: | ||
Now we will create a bridge called br0 | Now we will create a bridge called br0 | ||
| Line 182: | Line 237: | ||
{{Cmd | brctl addif br0 dummy0 }} | {{Cmd | brctl addif br0 dummy0 }} | ||
Next, let's give that bridged interface a reason to | Next, let's give that bridged interface a reason to exist: | ||
{{ Cmd | ifconfig br0 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up}} | {{ Cmd | ifconfig br0 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up}} | ||
Create a file for your container | Create a file for your container. Let's say /etc/lxc/bridgenat.conf, with the following settings. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
lxc. | lxc.net.0.type = veth | ||
lxc. | lxc.net.0.flags = up | ||
lxc. | lxc.net.0.link = br0 | ||
lxc. | lxc.net.0.name = eth1 | ||
lxc. | lxc.net.0.ipv4.address = 192.168.1.2/24 192.168.1.255 | ||
lxc.net.0.ipv4.gateway = 192.168.1.1 | |||
lxc.net.0.veth.pair = veth-if-0 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
and build your container with that file | and build your container with that file: | ||
{{ Cmd | lxc-create -n alpine -f /etc/lxc/bridgenat.conf -t alpine }} | {{ Cmd | lxc-create -n alpine -f /etc/lxc/bridgenat.conf -t alpine }} | ||
You should now be able to ping your container from your | You should now be able to ping your container from your host, and your host from your container. | ||
Your container needs to know where to push traffic that isn't within it's subnet. To do so, we tell the container to route through the bridge interface br0 | Your container needs to know where to push traffic that isn't within it's subnet. To do so, we tell the container to route through the bridge interface, br0 | ||
From inside the container run | From inside the container run | ||
{{ Cmd | route add default gw 192.168.1.1 }} | {{ Cmd | route add default gw 192.168.1.1 }} | ||
The next step is | The next step is to push the traffic coming from your private subnet over br0 out through your internet facing interface, or any interface you chose | ||
We are messing with your IP tables here, so make sure these settings don't conflict with anything you may have already set up | We are messing with your IP tables here, so make sure these settings don't conflict with anything you may have already set up. | ||
Say eth0 was your internet facing network interface, and br0 is the name of the bridge you made earlier | Say eth0 was your internet facing network interface, and br0 is the name of the bridge you made earlier. We'd do this: | ||
{{ Cmd | echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward | {{ Cmd | echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward | ||
| Line 224: | Line 281: | ||
=== Using static IP === | === Using static IP === | ||
If you're using static IP, you need to configure this properly on guest | If you're using static IP, you need to configure this properly on the guest /etc/network/interfaces. To stay in line with the above example, modify ''/var/lib/lxc/guest1/rootfs/etc/network/interfaces'' | ||
from | from | ||
| Line 288: | Line 345: | ||
=== VirtualBox === | === VirtualBox === | ||
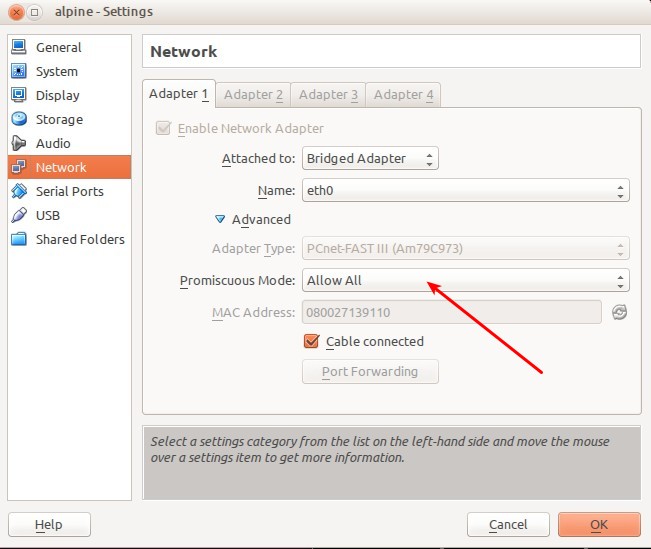
In order for network to work on containers you need to set "Promiscuous Mode" to "Allow All" in VirtualBox settings for the network adapter. | In order for the network to work on containers, you need to set "Promiscuous Mode" to "Allow All" in VirtualBox settings for the network adapter. | ||
[[File:VirtualBoxNetworkAdapter.jpg]] | [[File:VirtualBoxNetworkAdapter.jpg]] | ||
=== postgreSQL === | === postgreSQL === | ||
| Line 310: | Line 366: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Howto-lxc-simple]] | * [[Howto-lxc-simple]] | ||
[[Category:Virtualization]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:43, 14 July 2025
Linux Containers (LXC) provides containers similar to BSD Jails, Linux VServers and Solaris Zones. It gives the impression of virtualization, but shares the kernel and resources with the "host". You can use lxc directly or through LXD.
Installation
Install the required packages:
apk add lxc bridge lxcfs lxc-download xz
If you want to create containers other than Alpine, you'll need lxc-templates:
apk add lxc-templates
Upgrading from 2.x
Starting with Alpine 3.9, we ship LXC version 3.1. LXC 3.x has major changes which can and will break your current setup. LXC 3.x will NOT ship with legacy container templates. Check your current container configs to see if you have any includes pointing to files that don't exist (shipped by legacy templates). For example if you use Alpine containers created with the Alpine template, you'll need to install:
apk add lxc-templates-legacy-alpine
Also make sure you convert your LXC config files to the new 2.x format (this is now required).
lxc-update-config -c /var/lib/lxc/container-name/config
Make sure you have removed cgroup_enable from your cmdline as this will fail to mount cgroups and fail LXC service.
Prepare network on host
Install the lxc-bridge package to create the lxcbr0 bridge and configure the forwarding routes using iptables
apk add lxc-bridge iptables
Enable the dnsmasq OpenRC service at boot and start it
rc-update add dnsmasq.lxcbr0 boot service dnsmasq.lxcbr0 start
If you dont want to forward the routes, add DISABLE_IPTABLES="yes" to the /etc/conf.d/dnsmasq.lxcbr0 file
Assign static IP for a container
Using the dnsmasq method you can leave the container interface asking for DHCP as it is. You will just need to set the DHCP server asnwers.
By editing the file /etc/lxc/dnsmasq.conf and add the hostname (container name) and desired ip
dhcp-host=guest1,10.0.3.4 dhcp-host=guest2,10.0.3.5
Restart the service
service dnsmasq.lxcbr0 restart
Create a guest
Picking from the list
lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t download
And just pick from the list. lxc-download and xz can be uninstalled after you are done.
Alpine Template
lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t alpine
This will create a /var/lib/lxc/guest1 directory with a config file and a rootfs directory.
Note: by default, the alpine template does not have networking service on, you will need to add it using lxc-console
If running on x64 compatible hardware, it is possible to create a 32bit guest:
lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t alpine -- --arch x86
Debian template
In order to create a debian template container you'll need to install some packages:
apk add debootstrap rsync
You'll need to turn off some grsecurity chroot options otherwise the debootstrap will fail:
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chroot echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mount echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mknod echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chmod
Remember to turn them back on, or simply reboot.
Now you can run:
SUITE=wheezy lxc-create -n guest1 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t debian
Setting a static IP
Since Debian Bullseye 11.3 you can't assign a static IP address using the lxc config file of the container because of a systemd change. To make it work with a configuration like the following
# grep net /var/lib/lxc/bullseye/config lxc.net.0.type = veth lxc.net.0.flags = up lxc.net.0.link = virbr1 lxc.net.0.ipv4.address = 192.168.1.111/24 lxc.net.0.ipv4.gateway = 192.168.1.1
You have to attach to the container and run
lxc-attach -n bullseye systemctl stop systemd-networkd systemctl disable systemd-networkd reboot
After the reboot the IP address should be set correctly. This can be confirmed using the lxc-ls command
# lxc-ls -f NAME STATE AUTOSTART GROUPS IPV4 IPV6 UNPRIVILEGED bullseye RUNNING 1 - 192.168.1.111 - false
Ubuntu template
Alpine has not contained grsec for a long time (Discuss) |
In order to create an ubuntu template container, you'll need to turn off some grsecurity chroot options:
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_caps echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chroot echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mount echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_mknod echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/grsecurity/chroot_deny_chmod
Remember to turn them back on, or simply reboot.
Now you can run (replace %MIRROR% with the actual hostname, for example: http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/)
lxc-create -n guest2 -f /etc/lxc/default.conf -t ubuntu -- -r xenial -a amd64 -u user --password secretpassword --mirror $MIRROR

Unprivileged LXC images (Alpine / Debian / Ubuntu / Centos etc..)
To enable unprivileged containers, one must create a uidgid map:
echo root:1000000:65536 | tee -a /etc/subuid echo root:1000000:65536 | tee -a /etc/subgid
This creates a uid and gid map for the root user starting at 1000000 with a size of 65536.
To configure containers to use this mapping, add the following lines to the configuration:
lxc.idmap = u 0 1000000 65536 lxc.idmap = g 0 1000000 65536
This can be in the global or container-specific configuration.
To create an unprivileged lxc container, you need to use the download template. The download template must be installed:
apk add gnupg xz lxc-download lxc-create -n container-name -t download
choose the Distribution | Release | Architecture.
To be able to log in to a Debian container, you currently need to:
rm /lib/systemd/system/container-getty\@.service
You can also remove Systemd from the container.
Starting/Stopping the guest
First, you should enable the cgroup script:
rc-update add cgroups
If you don't want to reboot, you can start the service by running
rc-service cgroups start
Create a symlink to the /etc/init.d/lxc script for your guest.
ln -s lxc /etc/init.d/lxc.guest1
You can start your guest with:
rc-service lxc.guest1 start
Stop it with:
rc-service lxc.guest1 stop
Make it autostart at boot-up with:
rc-update add lxc.guest1
You can add to the container config: lxc.start.auto = 1
rc-update add lxc
to autostart containers with the lxc service only.
Connecting to the guest
By default, sshd is not installed. You'll have to attach to the container or connect to the virtual console. This is done with:
lxc-attach -n guest1
Type exit to detach from the container again (please check the grsec notes above)
Connect to virtual console
lxc-console -n guest1
To disconnect, press Ctrl+a q
Deleting a guest
Make sure the guest is stopped, then run:
lxc-destroy -n guest1
This will erase everything, without asking any questions. It is equivalent to:
rm -r /var/lib/lxc/guest1
Advanced
Creating a LXC container without modifying your network interfaces
The problem with bridging is that the interface you bridge gets replaced with your new bridge interface. Let's say you have interface eth0 that you want to bridge. Your eth0 interface gets replaced with the br0 interface that you create. It also means that the interface you use needs to be placed into promiscuous mode to catch all the traffic that could be destined to the other side of the bridge, which may not be what you want.
The solution is to create a dummy network interface, bridge that, and set up NAT so that traffic out of your bridge interface gets pushed through the interface of your choice.
Let's create that dummy interface (thanks to ncopa for talking me out of macvlan and pointing out the dummy interface kernel module)
modprobe dummy
This will create a dummy interface called dummy0 on your host. To create this interface on every boot, append "dummy" to /etc/modules:
Now we will create a bridge called br0
brctl addbr br0 brctl setfd br0 0
and then make that dummy interface one end of the bridge
brctl addif br0 dummy0
Next, let's give that bridged interface a reason to exist:
ifconfig br0 192.168.1.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
Create a file for your container. Let's say /etc/lxc/bridgenat.conf, with the following settings.
lxc.net.0.type = veth lxc.net.0.flags = up lxc.net.0.link = br0 lxc.net.0.name = eth1 lxc.net.0.ipv4.address = 192.168.1.2/24 192.168.1.255 lxc.net.0.ipv4.gateway = 192.168.1.1 lxc.net.0.veth.pair = veth-if-0
and build your container with that file:
lxc-create -n alpine -f /etc/lxc/bridgenat.conf -t alpine
You should now be able to ping your container from your host, and your host from your container.
Your container needs to know where to push traffic that isn't within it's subnet. To do so, we tell the container to route through the bridge interface, br0 From inside the container run
route add default gw 192.168.1.1
The next step is to push the traffic coming from your private subnet over br0 out through your internet facing interface, or any interface you chose
We are messing with your IP tables here, so make sure these settings don't conflict with anything you may have already set up.
Say eth0 was your internet facing network interface, and br0 is the name of the bridge you made earlier. We'd do this:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward iptables --table nat --append POSTROUTING --out-interface eth0 -j MASQUERADE iptables --append FORWARD --in-interface br0 -j ACCEPT
Now you should be able to route through your bridge interface to the internet facing interface of your host from your container, just like at home!
You could also have a dhcp server running on your host, and set it up to give IP addresses from your private subnet to any container that requests it, and then have one template for multiple alpine LXC containers, perfect for alpine development :)
Using static IP
If you're using static IP, you need to configure this properly on the guest /etc/network/interfaces. To stay in line with the above example, modify /var/lib/lxc/guest1/rootfs/etc/network/interfaces
from
#auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
to
#auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address <lxc-container-ip> # IP which the lxc container should use
gateway <gateway-ip> # IP of gateway to use, mostly same as on lxc-host
netmask <netmask>
mem and swap
vim /boot/extlinux.conf
APPEND initrd=initramfs-3.10.13-1-grsec root=UUID=7cd8789f-5659-40f8-9548-ae8f89c918ab modules=sd-mod,usb-storage,ext4 quiet cgroup_enable=memory swapaccount=1
checkconfig
lxc-checkconfig
Kernel configuration not found at /proc/config.gz; searching... Kernel configuration found at /boot/config-3.10.13-1-grsec --- Namespaces --- Namespaces: enabled Utsname namespace: enabled Ipc namespace: enabled Pid namespace: enabled User namespace: missing Network namespace: enabled Multiple /dev/pts instances: enabled --- Control groups --- Cgroup: enabled Cgroup clone_children flag: enabled Cgroup device: enabled Cgroup sched: enabled Cgroup cpu account: enabled Cgroup memory controller: missing Cgroup cpuset: enabled --- Misc --- Veth pair device: enabled Macvlan: enabled Vlan: enabled File capabilities: enabled Note : Before booting a new kernel, you can check its configuration usage : CONFIG=/path/to/config /usr/bin/lxc-checkconfig
VirtualBox
In order for the network to work on containers, you need to set "Promiscuous Mode" to "Allow All" in VirtualBox settings for the network adapter.
postgreSQL
Inside the container run:
chmod go+w /dev/null
to fix
rc-service postgresql start
openVPN
see Setting_up_a_OpenVPN_server#openVPN_and_LXC
LXC 1.0 Additional information
Some info regarding new features in LXC 1.0
https://www.stgraber.org/2013/12/20/lxc-1-0-blog-post-series/